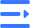
45 Degree Vs 90 Degree Elbow
Updated : Jun. 24, 202545 degree elbow vs 90 degree elbow — understanding the difference is crucial for designing efficient piping systems. These two common elbows are widely used in petrochemical, power, and pneumatic conveying industries to change flow direction.
The angle, radius, and layout of an elbow directly affect pressure drop, flow rate, and system lifespan.
This article compares the features, applications, pros, and cons of 45° and 90° elbows to help you choose the right pipe fitting solution.
What is an elbow
A pipe elbow is a type of fitting used to change the direction of flow in a piping system. It connects two pipes and redirects the flow of liquid or gas.
Elbows come in different angles, with 45-degree and 90-degree being the most commonly used.

Materials and manufacturing
Elbows are made from various materials, including titanium, aluminum alloys, carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, and PVC, depending on the specific application. Common manufacturing methods include forging, casting, or welding.
-
Carbon Steel
Low cost and high strength; ideal for oil, gas, and industrial pipelines.
-
Stainless Steel
Excellent corrosion resistance; widely used in food, chemical, and marine industries.
-
Alloy Steel
High strength and heat resistance; suitable for high-pressure or high-temperature environments.
-
Titanium
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant; used in exhaust systems, aerospace, and chemical industries.
-
Aluminum Alloy
Lightweight and easy to install; commonly used in HVAC and structural piping.
-
PVC / Plastic
Corrosion-resistant and easy to handle; suitable for drainage and low-pressure transport systems.
What is a 45 degree elbow?
-

A 45-degree elbow is designed to connect two pipes at a 45° angle, allowing for a smoother directional change.
Features of 45-degree elbows
- Smooth flow: The gradual curve minimizes turbulence and supports steady flow.
- Reduced pressure loss: Helps maintain internal pressure levels in the system.
- Minimal space requirement: Requires less installation space than sharper-angled fittings.
Applications of 45-degree elbows
- HVAC systems: Ideal for air handling and ventilation, ensuring efficient airflow.
- Plumbing: Provides smooth transitions in water supply pipelines.
- Chemical processing: Used in systems that need gentle directional changes.



In systems where flow efficiency is critical, 45-degree elbows are often preferred. Their gentle bend helps reduce wear on the piping system.
Disadvantages of 45-degree elbows
While they minimize impact damage, 45-degree elbows are more prone to wear. This can lead to issues like plastic sagging or fragile particles, accelerating elbow erosion.
The smaller angle may also require more space, which can be a concern for compact installations.
What is a 90 degree elbow?
-

A 90-degree elbow is designed to connect two pipes at a right angle, allowing for a sharp change in direction.
Features of 90-degree elbows
- Right-angle connection: Creates a sharp turn to redirect flow at 90 degrees.
- Increased pressure drop: May cause more turbulence and energy loss.
- Space-saving: Allows compact installation in tight spaces.
Applications of 90-degree elbows
- Plumbing and drainage: Commonly used to redirect flow in wastewater systems.
- Industrial piping: Ideal for flow redirection in confined layouts.
- Oil and gas: Used in high-pressure systems where space is limited.



90-degree elbows are typically chosen for space-constrained setups where the system can handle increased turbulence and pressure drop.
Disadvantages of 90-degree elbows
The sharp turn of a 90-degree elbow increases the risk of impact damage to both the elbow and the material.
Heavier materials lose energy and speed upon collision, requiring more force to keep bulk solids moving through the pipeline.
Key differences between 45° and 90° elbows
While both elbows serve to change the direction of flow in piping systems, they differ in several key ways:
Angle and bend radius
- A 45° elbow provides a gentler change in direction with a larger bend radius.
- A 90° elbow makes a sharp turn with a tighter radius.
This geometric difference directly impacts how each elbow is used in pipeline layouts.
Flow characteristics (turbulence and pressure drop)
- Flow through a 45° elbow is smoother, generating less turbulence and lower pressure loss.
- In contrast, a 90° elbow creates more turbulence and a greater pressure drop due to the abrupt turn.
As a result, systems with multiple 90° elbows may require stronger pumps to maintain flow rate.
Wear and erosion
- The smoother path of a 45° elbow means less impact force on the pipe wall, reducing wear at the turn.
- A 90° elbow causes a sudden redirection, increasing impact and stress at the inner bend, which may lead to erosion.
In solid-particle transport, sharp turns can cause particle breakage and accelerate inner wall abrasion.
Space configuration
- A 45° elbow needs a longer straight section to complete the bend, which makes the pipe layout more gradual but more space-consuming.
- A 90° elbow creates a right-angle turn in a shorter span, saving space and allowing flexible routing in tight areas.

This gives 90° elbows a clear advantage in compact and crowded installations.
Installation and number of joints
- To achieve a near 90° turn with 45° elbows, two are usually joined together. This increases the number of joints, potential leak points, and installation steps.
- A single 90° elbow completes the turn with one fitting and fewer connections.
Fewer joints mean easier installation and lower leak risk—but with trade-offs in other performance aspects.
Maintenance cost comparison
- 45° elbow: Smoother flow with less turbulence and wear results in lower maintenance needs and long-term cost savings.
- 90° elbow: The sharper turn causes higher stress and debris buildup, requiring more frequent inspections and replacements, increasing long-term maintenance costs.
Project selection: how to choose between 45° and 90° elbows
Evaluate flow requirements
If your main goal is to reduce turbulence, lower pressure drop, and save on pumping energy, a 45° elbow is the better choice.
If the system can tolerate higher pressure loss or already has enough pressure margin, a 90° elbow may be used for easier layout.
Consider space limitations
When planning the pipeline layout, assess the available space.
In tight areas where pipes must turn close to walls or equipment, the compact turn of a 90° elbow is more valuable.
If space is not an issue, using a 45° elbow—or two in sequence for a near 90° bend—allows for smoother transitions.
Media and working conditions
Take into account the characteristics of the media being transported.
For solid particles or high-viscosity fluids, the gentler turn of a 45° elbow reduces impact damage to both media and fittings.
For gases or clean, low-viscosity liquids, a 90° elbow usually works fine. For high-speed flows, using a long-radius 90° elbow can improve flow performance.
Installation and maintenance
Balance ease of installation with long-term maintenance.
A 45° elbow may need more fittings and joints, while a 90° elbow uses fewer materials and is simpler to install.
More joints mean more potential leak points. To ensure reliability, weigh installation convenience against risk.
Also consider maintenance: in high-velocity or abrasive service, 90° elbows may wear out faster and require more frequent replacement.
If you aim to reduce downtime, choose the elbow type that best withstands your media over time.
Standards and compliance
Make sure your elbow selection meets applicable engineering codes and industry standards.
Some sectors or local regulations specify what type of elbow must be used.
For example, drainage systems may require long-radius elbows to reduce clogging.
Always align your selection with industry needs and local rules.
Various elbows supplied by Chalco
At Chalco, we offer a wide range of elbow products in multiple materials, including titanium alloys (Gr2, Gr5), aluminum alloys (6061, 6082), as well as stainless steel (304, 316), alloy steel, copper, and brass—meeting the needs of diverse industries and operating conditions.

45° elbow

90° elbow

180° return bend

Butt weld elbow

Socket weld elbow

Threaded elbow
Whether you're designing a high-pressure chemical pipeline, a compact HVAC system, or a corrosion-resistant exhaust setup, Chalco provides durable elbow solutions that meet international standards and ensure long-lasting performance. Quick Quote
How to calculate pipe elbow dimensions (with formulas)
Purchasing elbows with incorrect dimensions can severely impact your operations. It may lead to excessive wear, reduced performance, or system downtime—all of which increase costs and lower profitability.
| Elbow Type | Elbow Angle | Calculation Formula |
| Long Radius (LR) | 90° | A = 1.5 × NPS × 25.4 |
| Long Radius (LR) | 45° | A = 0.75 × NPS × 25.4 |
| Short Radius (SR) | 90° | A = 1.0 × NPS × 25.4 |
| Short Radius (SR) | 45° | A = 0.5 × NPS × 25.4 |
To calculate the center-to-end distance of an NPS 2 (2-inch) long radius 90° elbow:
A = 1.5 × 2 × 25.4 = 76.2 mm
With the above calculations, you can plan ahead before purchasing elbows, avoid rework and losses, and ensure long-term efficient operation of your system.
Frequently asked questions: 45° elbow vs 90° elbow
Is a 45-degree elbow better than a 90-degree elbow?
Each has its pros and cons. A 45° elbow offers smoother flow and less wear, while a 90° elbow is more compact and easier to install. The best choice depends on available space, fluid type, and system requirements.
Is it better to use two 45° elbows instead of one 90° elbow?
If space allows, two 45° elbows can provide a gentler directional change and reduce pressure loss. However, this increases the number of joints and installation complexity.
Choose two 45° elbows for better flow efficiency, or a single 90° elbow for tight spaces and simpler piping.
What’s the price difference between 45° and 90° elbows?
In general, a single 45° elbow is slightly cheaper than a 90° elbow. But using two 45° elbows to replace one 90° can increase total cost due to added connections and labor.
What are the common sizes of 45° and 90° elbows?
Popular sizes include 1/2", 3/4", 1", 2", 3", 4", 6", 8", 10", and 12".
For long radius elbows, a 90° elbow has a center-to-end distance of about 1.5 × NPS × 25.4 mm, while a 45° elbow is approximately 0.75 × NPS × 25.4 mm.
How much flow is lost in a 90° elbow?
A 90° elbow causes more pressure drop than a 45° elbow—typically 10%–30% higher depending on flow speed, fluid type, and pipe diameter. The effect is especially noticeable in high-velocity or solid-particle systems.
What's the difference between long radius and short radius elbows?
Long radius elbows (1.5×NPS) provide smoother flow and lower pressure drop. Short radius elbows (1.0×NPS) save space but cause more turbulence and wear.
Whether you're working with a complex industrial system or a simple piping setup, understanding these differences helps you choose the right elbow for your application.
From smooth HVAC flow to compact industrial layouts, the right elbow improves your system's efficiency and reliability.