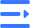
Titanium Dental Implants Guide
Updated : Jun. 24, 2025Titanium dental implants are a strong, long-lasting solution for missing teeth.
They fuse naturally with the jawbone, look and feel like real teeth, and won't slip like dentures. Learn their key benefits, costs, and whether they're right for you.
Benefits of titanium dental implants
Biocompatibility
Titanium's exceptional biocompatibility is a key reason for the success of dental implants. It's non-toxic and integrates naturally with human tissue, reducing the risk of rejection or inflammation. This promotes faster, healthier healing after surgery.
Titanium also forms a strong bond with surrounding bone, creating a stable foundation. This dramatically improves the long-term success rate of dental implants.
Strength and durability
Titanium dental implants are as strong as natural tooth roots. They can handle the heavy biting and chewing forces of daily use without breaking or loosening.
Their high toughness helps prevent fractures or deformation. It also protects nearby bone structures from excessive stress or damage.
Corrosion resistance
Titanium forms a stable oxide layer that resists saliva, food acids, and bacterial corrosion. This protects the implant from chemical wear and stops metal ions from leaching into the body.
That means the implant stays safe and stable for years, without harming surrounding tissues.
Low allergenic risk
Titanium is highly inert, making it one of the most hypoallergenic metals used in medicine. It rarely triggers allergic reactions, even in sensitive patients.
Unlike some metals, titanium doesn't release ions that cause irritation or inflammation. It can remain safely in the body for decades.
Osseointegration
Titanium bonds directly with jawbone through a process called osseointegration. This forms a secure, long-lasting anchor that holds the implant firmly in place. Better integration means better stability—and longer implant life.
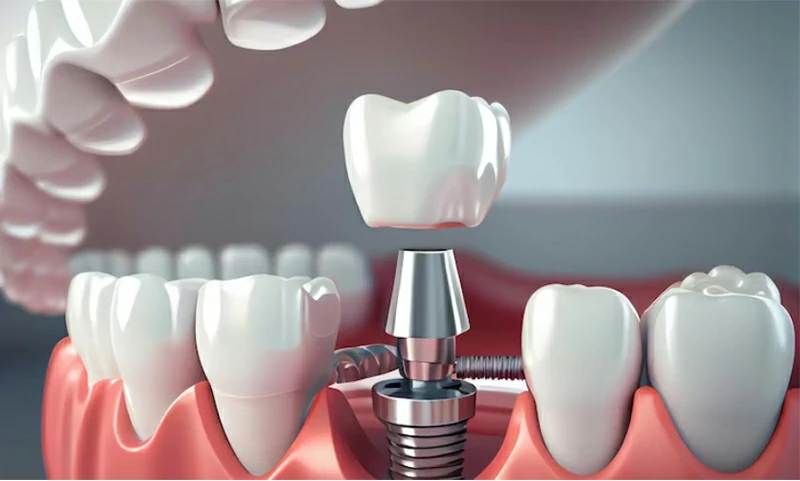
Versatility
Titanium dental implants come in many shapes and sizes. They can be customized to fit different bone structures and treatment needs.
Whether you're missing one tooth, several, or an entire arch, titanium implants offer a reliable, adaptable solution. They also work well with crowns, bridges, and overdentures.
Low titanium dental implant cost over time
While the upfront titanium dental implant cost may seem high, the long-term value is unbeatable. With proper care, they can last a lifetime—no need for replacements or costly repairs.
Many clinics offer flexible insurance plans or monthly payment options. This makes restoring your smile both affordable and achievable.
High success rate
Titanium has been used in dental implants since the 1960s. Decades of clinical data confirm its safety and effectiveness.
Studies show titanium implants have a success rate of over 95% within 10 years—one of the highest in restorative dentistry.
Better oral health and quality of life
Titanium implants feel and function like real teeth. You don't need to remove them for cleaning—they're cared for just like natural teeth.
They also look great. Seamlessly blending with your gums and crowns, they restore confidence, improve chewing, and enhance daily life.
Drawbacks of titanium dental implants
Surgical risks
Titanium dental implants require a surgical procedure, which carries inherent risks despite their high success rate. Possible complications include infection, poor healing, or failure of the implant to bond with the bone.
In complex cases, inadequate anatomical assessment may lead to nerve damage, bleeding, or sinus perforation. Improper bone volume or angulation may also cause instability and long-term failure.
The good news? These risks are rare when the surgery is performed by an experienced implant dentist. Thorough pre-op planning and precise technique greatly reduce complications.
Allergic reactions
Titanium is highly biocompatible, and allergic reactions are extremely rare. However, in very isolated cases, patients may experience sensitivity or immune responses.
Symptoms may include localized inflammation, pain, or discomfort around the implant site. In rare situations, this may lead to implant failure or poor osseointegration.
Most such issues are actually caused by infections or mechanical stress—not true titanium allergies. Pre-surgery allergy screening and medical history review help identify risks and guide safer treatment.
Aesthetic limitations
Titanium implants may have limitations in highly visible areas. The metallic base can sometimes show through thin or receding gum tissue, causing a grayish hue.
This is more noticeable in the front teeth area or patients with a high smile line. In such cases, aesthetic concerns may require special design considerations or alternative materials like zirconia.
What types of titanium dental implants are available?
Titanium dental implants are mainly classified into commercially pure titanium (CPTi) and titanium alloys.
Commercially Pure Titanium (CPTi)
CPTi contains 98–99.9% pure titanium and offers the highest biocompatibility and corrosion resistance among implant materials.
Contact us now
- Grade 3: Offers good strength and excellent corrosion resistance. Suitable for implants requiring moderate mechanical performance.
- Grade 4: The strongest grade of CPTi, widely used in dental implant bodies. It balances excellent biocompatibility with load-bearing capacity.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium alloys are formed by adding elements to titanium to improve strength, hardness, and ductility—making them ideal for load-bearing applications.
Contact us now
Common titanium alloys used in implants include:
- Ti-6Al-4V: The most widely used titanium alloy in medical implants due to its exceptional strength, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance.
- Ti-5Al-2.5Fe: Offers similar strength to Ti-6Al-4V but with better ductility and machinability.
- Ti-3Al-2.5V: Combines strength and biocompatibility with a lightweight structure, making it suitable for pediatric orthopedic implants.
Material selection depends on clinical needs and patient-specific factors. CPTi is favored for its compatibility with human tissue, while titanium alloys are chosen for their enhanced mechanical properties.
Factors like bone density, implant size, and expected load also influence the choice of material.
As one of China's largest titanium material manufacturers, we welcome inquiries for medical-grade titanium implant materials.
Choosing between titanium and zirconia (ceramic) implants
Titanium and zirconia are the two most common materials for dental implants. Each has unique benefits and suits different patient needs and aesthetic goals.
For patients with thin gums or high cosmetic demands, zirconia implants offer a natural white color that blends better with soft tissue.
This helps reduce the risk of metal showing through the gum line. Studies also suggest zirconia surfaces attract fewer bacteria, potentially lowering inflammation risk. Its osseointegration performance is comparable to titanium.
However, titanium implants remain the gold standard in clinical practice. They are backed by decades of success, broader indications, and a higher overall success rate.
In contrast, zirconia implants come with higher production costs, stricter technical requirements, and more limited clinical use.
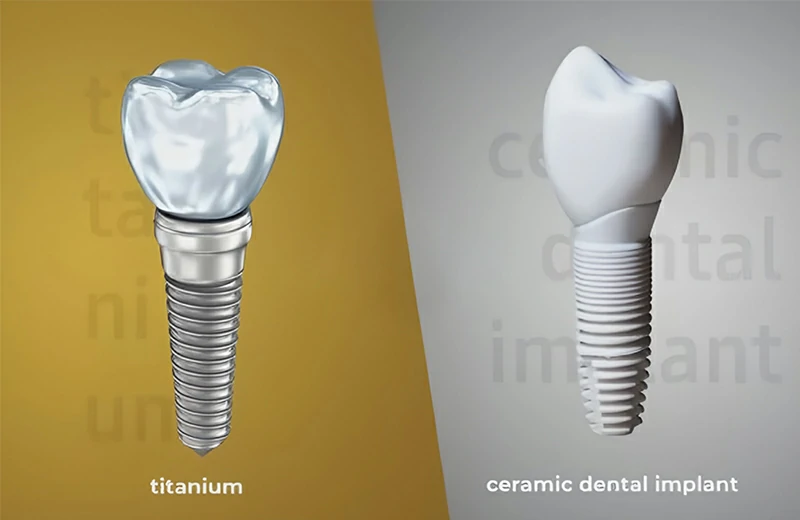
Understanding the differences between titanium and zirconia implants is key to choosing the right solution for your needs. Here’s how they compare:
| Feature | Titanium implants | Ceramic (zirconia) implants |
| Durability | Highly durable | Less durable |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent integration | Excellent integration |
| Material | Metallic titanium | White, aesthetic ceramic |
| Color | Metallic, may show under gums | White and gum-friendly |
| Allergy risk | Possible metal sensitivity | Hypoallergenic |
| Long-term success | Proven over decades | Newer, limited long-term data |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher cost |
Therefore, when choosing an implant material, patients should consider their oral anatomy, aesthetic goals, and budget—making the best decision under the guidance of a qualified dental professional.
Surface treatment technologies for titanium dental implants
Surface roughening (sandblasting, acid etching)
Titanium implants are often sandblasted or acid-etched to create a micro-rough surface. This texture helps bone cells grip the implant more effectively, promoting faster and stronger osseointegration.
Contact us now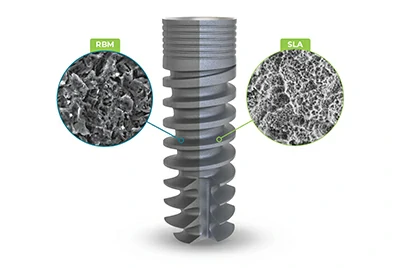

Alkaline treatment (enhanced bioactivity)
By treating the titanium surface with concentrated sodium hydroxide (NaOH), it gains a negative charge that attracts calcium ions from body fluids. This encourages natural deposition of hydroxyapatite, improving bone bonding.
Contact us nowAnodic oxidation (thickened oxide layer)
Electrochemical anodization forms a dense, porous titanium oxide film on the surface. This boosts corrosion resistance and enhances bone cell attachment, improving implant stability.
Contact us now
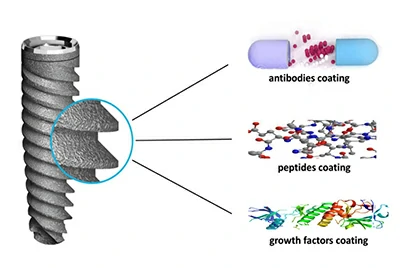
Coating technologies (hydroxyapatite / diamond-like carbon)
Bioactive coatings mimic the mineral content of natural bone. These coatings are especially useful in areas with poor bone quality, helping the implant fuse more quickly and securely with the jawbone.
How are titanium dental implants placed?
Consultation
The process begins with a detailed consultation. Your dentist will assess your oral condition, bone volume, and overall health. The goal is to create a personalized treatment plan that fits your restoration needs.
Placement
The titanium implant is precisely placed into the jawbone under local anesthesia. This step is usually minimally invasive, safe, and performed by an experienced dental surgeon to ensure stability for the final restoration.
Healing
During healing, the implant undergoes osseointegration—a natural process where bone tissue fuses with the titanium post. This takes several weeks to a few months and is critical for long-term success.
Final restoration
Once healing is complete, a custom dental crown, bridge, or full denture is placed on the implant. This final step restores both function and appearance, giving you a natural-looking and confident smile.
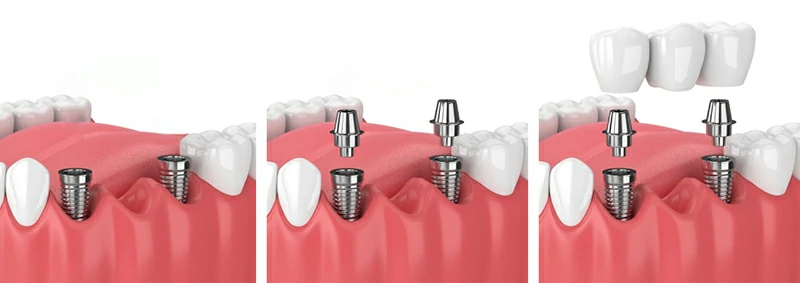
Do titanium implants require special care?
Implant failure can happen—but it's often preventable with proper oral hygiene.
Gum disease is a major risk, as healthy gums are essential for supporting the implant. To protect your new teeth (and your natural ones), maintain excellent daily care.
Brush and floss at least twice a day. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to keep harmful bacteria away from the gumline and implant area. This prevents infection and helps preserve long-term stability.
Common questions about titanium implants
Do titanium implants cause cancer?
No. There is no scientific evidence linking titanium implants to cancer. Titanium is highly biocompatible and has been safely used in dentistry and orthopedics for nearly 60 years.
What is a Grade 5 titanium implant?
Grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, contains 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium. It offers high strength and excellent fatigue resistance.
Its medical-grade form, Grade 23 (ELI), is specially purified for human use—combining mechanical strength with biological safety. It’s often used in abutments and implant screws.
Will titanium implants set off metal detectors?
Rarely. Titanium is non-magnetic and contains no iron, so it usually doesn't trigger airport or security metal detectors.
Titanium is also MRI-safe. It won't interfere with imaging or pose safety risks during scans.
Are titanium allergies common?
Extremely rare. Studies show that only about 0.6% of dental patients experience mild allergic reactions to titanium.
If you have a known metal allergy, pre-treatment allergy testing can help ensure implant safety.
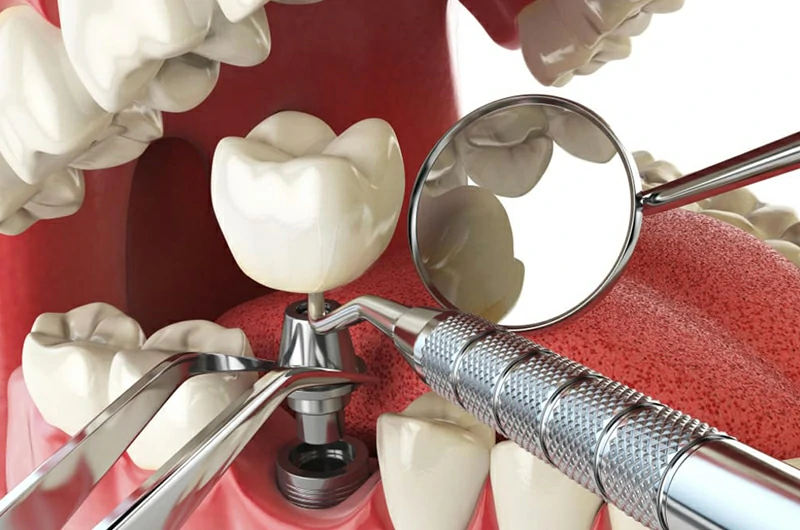
How soon can I return to normal life after surgery?
Most patients can resume daily activities and work within 1–2 days after surgery.
Full bone integration takes 3–6 months. During this period, avoid hard chewing or local pressure to allow the implant to bond securely with the jawbone.