Titanium Clad
Updated : Oct. 23, 2025Titanium clad material combines titanium's corrosion resistance with the strength of the base metal. It cuts cost by 40–60% compared with solid titanium.
Large plates and custom parts are supplied in compliance with ASTM B898 / EN 13445-2, making it an ideal choice for chemical, energy, and offshore industries.
Titanium clad specifications
- ASTM B898 / ASME SB898
- NB/T 47002.3-2010
- GB/T 8547,GB/T 8546,GB/T 8165,GB/T 13238
- EN 13445-2
- ASME SA263-265,ASTM B432
Titanium clad popular product categories
We supply the full range of titanium clad products and accessories, covering plate/bar/tube/wire, tube sheets, heads, flanges, shell sections, rolled parts, and custom components.
We support drawing-based customization, third-party witnessing, and global shipping.
表格中的产品为锚点, 点击跳转产品对应的h3
| Product | Main form | Size | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium clad carbon steel | Plate, tube sheet, head, flange, rolled parts | Thickness 8–120 mm; width ≤3000 mm; length ≤10000 mm | ASTM B898 / ASME SB898 / NB/T 47002.3 |
| Titanium clad copper | Plate, bus bar/bar, tube, wire, cathode plate, conductive beam | Titanium layer 0.6–3.0 mm; length ≤12 m | ASTM B898, ASTM B432 |
| Titanium clad aluminum | Plate/coil, transition joint, bar, anode, honeycomb/corrugated | Thickness 1–12 mm; width ≤3000 mm; length ≤12 m | ASTM B898, EN 13445-2 |
| Titanium clad nickel | Plate, tube sheet, head/flange, conductive backplate | Thickness 8–120 mm (up to 500); width ≤4200; length ≤12000 | ASTM B898 / B265 (Ti) / B162 (Ni) |
| Titanium clad stainless steel | Plate, tube sheet, head, flange, shell section, rolled parts | Total thickness 8–120 mm; titanium layer 1–15 mm; width ≤3000; length ≤10000 | ASTM B898 |
| Titanium clad zinc | Plate, coil, custom parts | Thickness 6–80 mm; titanium layer 0.5–3 mm; zinc layer ≥5 mm | ASTM B898 |
Titanium clad carbon steel
Complying with ASTM B898, ASME SB898, and NB/T 47002.3 standards.
Titanium clad carbon steel plate combines titanium's corrosion resistance with the high strength of carbon steel, reducing cost by 40–60% compared with solid titanium.
Contact us now
- Cladding material: Gr 1 titanium
- Base material: SA516 Gr 70
- Other common bases: Q235B, Q345R, 16MnR, 20R
- Carbon steel surface: polished, ground, or sandblasted for better welding and assembly
- Process: explosive bonding with hot rolling / cold rolling
- Thickness 8–120 mm, width ≤3000 mm, length ≤10000 mm
It is suitable for severe corrosion media under ambient and medium temperatures, such as pressure vessels, storage tanks, heat exchangers, reactors, FGD desulfurization units, salt chemical plants, and wet chlorine environments.

Titanium/Steel Tube Sheet

Titanium Steel Head

Titanium Steel Clad Head
Large plate sizes can be customized to fit various vessels and equipment.
Titanium clad copper
Longer service life, lower pressure drop, and reduced energy consumption. It significantly cuts downtime and maintenance costs, improving production stability and efficiency.
With nearly 100% IACS conductivity and excellent resistance to chlorides, acids, and seawater, titanium clad copper ensures long-lasting, reliable performance.
Contact us now
- Outer layer: Ti Gr1 / Gr2
- Core: C11000 (ETP) or C10200 (OFHC) copper
- Cladding thickness: 0.6–3.0 mm (typical 1.0–2.5 mm, customizable)
- Length: ≤12 m
- Process: explosive bonding / roll bonding
The copper core provides nearly 100% IACS high conductivity for efficient current transfer.
The titanium layer maintains long-term corrosion resistance in chloride, acid, alkali, and seawater environments, ensuring stable equipment operation.
Applications include solvent extraction electrowinning (SX-EW), electroplating lines, chlor-alkali processes, cathodic protection systems, and seawater or wastewater treatment.

Titanium Clad Copper Plate

Titanium Clad Copper Bar

Titanium Clad Copper Tube

Titanium Clad Copper Wire

Cathode Plate

Conductive Beam
We supply a full range of titanium clad copper products — plate, bar/bus bar, tube, wire, as well as cathode plates, conductive beams, and custom parts.
They are widely used in electrolysis, electroplating, chlor-alkali, and water treatment under highly corrosive, high-current conditions.
Titanium clad aluminum
Titanium aluminum clad material consists of two bonded metal layers: a titanium core and an aluminum outer layer.
Using metallurgical processes such as hot rolling or explosive welding, the two layers are permanently joined.
Compared with solid titanium, titanium clad aluminum saves raw material, is easier to process and transport, and greatly reduces total equipment cost.
Contact us now
- Cladding (titanium layer): Ti Gr1 / Gr2 (other grades customizable)
- Core (aluminum base): industrial pure aluminum / aluminum alloy
- Process: explosive bonding / roll bonding
- Thickness: 1–12 mm (plate, larger laminates available)
- Width: ≤1200 mm (up to 3000 mm)
- Length: ≤12 m
- Surface: as-rolled / polished / sandblasted
All titanium clad aluminum products come with EN 10204 3.1 material certificates, UT inspection, and dimensional/thickness records.
They comply with ASTM B898 and EN 13445-2 international standards, with optional third-party witnessing available.

Titanium Clad Aluminum Plate

Aluminum-Titanium Transition Joint

Titanium Clad Aluminum Bar
Titanium clad nickel
Titanium nickel clad material provides dual protection. It resists chloride, acid, and alkali corrosion, while also withstanding sulfuric acid and alkaline media.
It ensures excellent corrosion resistance while greatly reducing material cost, making it more economical and efficient than pure titanium or pure nickel solutions.
Contact us now
- Cladding (titanium layer): Gr1, Gr2, Gr3, Gr7, Gr12, Gr16
- Core (nickel base): N2, N4, N6
- Process: explosive bonding / roll bonding / explosion + roll bonding
- Thickness range: total 8–120 mm (customizable up to 500 mm)
- Width: ≤4200 mm
- Length: ≤12000 mm
- Standards: ASTM B898, ASTM B265 (Ti), ASTM B162 (Ni), EN 10204 3.1/3.2
Compared with solid titanium or solid nickel plates, it offers higher cost performance, long service life, and minimal maintenance.
It is widely applied in chemical, metallurgy, electrolysis, electroplating, energy, marine, and aerospace industries.

Titanium Clad Nickel Plate

Pipe Fittings

Conductive Backplate
Please share your working conditions (medium/temperature/pressure), dimension drawings, and processing requirements.
We can provide selection advice, quotations, and sample support within 24 hours.
Titanium clad stainless steel
Titanium stainless steel clad is produced by explosive welding combined with hot rolling, firmly bonding one or two titanium layers onto a stainless steel base.
Contact us now
This composite material combines titanium's light weight, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance with the high strength, pressure resistance, and durability of stainless steel.
Our titanium clad stainless steel products are available in multiple forms, including clad plates, tube sheets, heads, flanges, shell sections, rolled parts, and custom components, meeting diverse equipment requirements.
- Cladding material: Gr1, Gr2, Gr3 (optional Gr5, Gr7, Gr11, Gr12)
- Base material: SUS 304, SUS 316L, SUS 410, etc.
- Total thickness: 8–120 mm (commonly 4–60 mm)
- Titanium layer thickness: 1–15 mm
- Width: ≤3000 mm (larger sizes available by splicing)
- Length: ≤10000 mm
- Surface finish: polished, sandblasted, pickled, or passivated (according to application and standards)
This material withstands acids, alkalis, chlorides, and seawater while remaining stable under high temperature and pressure.
It is an ideal choice for petrochemical, marine, energy, and pharmaceutical industries.

Flange

Titanium Stainless Steel Plate

Clad Cookware
Titanium clad zinc
Titanium zinc clad material combines titanium's strong corrosion resistance with zinc's anodic protection and weatherability.
It is lighter and more economical than solid titanium, making it ideal for long-term protection of large structures.
By merging titanium's corrosion resistance with zinc's sacrificial protection, titanium clad zinc offers a cost-effective and durable solution for marine, chemical, and architectural applications.
Contact us now
- Cladding (titanium layer): Gr1 / Gr2 (other grades customizable)
- Core (zinc base): industrial pure zinc or high-purity zinc alloy (N2 / N4, etc.)
- Process: explosive bonding / roll bonding
- Thickness: total 6–80 mm; titanium layer 0.5–3 mm; zinc layer ≥5 mm
- Width / length: wide plates and custom sizes available
- Standards: ASTM B898, GB/T series (clad plates)
Ti/Cu is best for electrolysis and electroplating.
Ti/Al works well in seawater and heat exchangers.
Ti/Ni resists strong acids, alkalis, and dual media.
Ti/SS serves clean and high-temperature environments.
Ti/CS delivers balanced corrosion resistance and cost.
Ti/Zn is designed for weathering and anodic protection.
Simply provide your working conditions (medium/temperature/pressure) and dimensions, and we will quickly recommend the right clad solution and provide a quotation.
Regular supply of titanium clad dimensions
Below are our main products that we supply and export year-round: titanium clad steel plate, titanium clad zinc plate, titanium clad copper plate, titanium clad aluminum plate, titanium clad nickel plate, and structural transition joints.

Titanium Clad Steel Plate

Titanium Clad Zinc Plate

Titanium Clad Copper Plate

Titanium Clad Aluminum Plate

Titanium Clad Nickel Plate

Structural Transition Joints
We supply Ti Gr1/2/7/11/12/17 cladding matched with base materials such as 304L/316L stainless steel, Nickel 200, P295GH/P355GH, and SA516-70N.
Projects cover energy, chemical, mining, and oil & gas industries. Standard plate thickness is available up to 19.1 mm (.750 in), with drawing-based fabrication supported.
| Products | Cladder | Backer | Industry | Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Grade 1 to 304L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 1 | 304L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 1 to 316L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 1 | 316L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 1 to Nickel 200 | Titanium Grade 1 | Nickel 200 | Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 1 to P295GH Steel | Titanium Grade 1 | P295GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 1 to P355GH Steel | Titanium Grade 1 | P355GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 1 to SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Titanium Grade 1 | SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 11 to 304L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 11 | 304L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 11 to 316L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 11 | 316L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 11 to Nickel 200 | Titanium Grade 11 | Nickel 200 | Chemical & Petrochemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 11 to P295GH Steel | Titanium Grade 11 | P295GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 11 to P355GH Steel | Titanium Grade 11 | P355GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 11 to SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Titanium Grade 11 | SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 12 to 304L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 12 | 304L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 12 to 316L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 12 | 316L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 12 to Nickel 200 | Titanium Grade 12 | Nickel 200 | Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 12 to P295GH Steel | Titanium Grade 12 | P295GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 12 to P355GH Steel | Titanium Grade 12 | P355GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 12 to SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Titanium Grade 12 | SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 17 to 304L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 17 | 304L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 17 to 316L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 17 | 316L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 17 to Nickel 200 | Titanium Grade 17 | Nickel 200 | Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 17 to P295GH Steel | Titanium Grade 17 | P295GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 17 to P355GH Steel | Titanium Grade 17 | P355GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 17 to SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Titanium Grade 17 | SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 2 to 304L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 2 | 304L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 2 to 316L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 2 | 316L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 2 to Nickel 200 | Titanium Grade 2 | Nickel 200 | Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 2 to P295GH Steel | Titanium Grade 2 | P355GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 2 to P355GH Steel | Titanium Grade 2 | P355GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 2 to SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Titanium Grade 2 | SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 7 to 304L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 7 | 304L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 7 to 316L Stainless Steel | Titanium Grade 7 | 316L Stainless Steel | Energy, Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 7 to Nickel 200 | Titanium Grade 7 | Nickel 200 | Chemical | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 7 to P295GH Steel | Titanium Grade 7 | P295GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 7 to P355GH Steel | Titanium Grade 7 | P355GH Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
| Titanium Grade 7 to SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Titanium Grade 7 | SA516 70N Carbon Steel | Minerals & Mining, Chemical, Oil & Gas | .750 in., 19.1 mm. |
If you need extra-wide, extra-long, non-standard laminates, or special grades, we can arrange cross-line production, sectional welding, and process alternatives to deliver a practical solution.
Whether you require standard sizes or large/customized products, we can provide fast selection and quotation within 24 hours, with sample delivery and witnessed inspection available.
Applications of titanium clad
Titanium cladding is widely used across industries, each with unique benefits:
Chemical / petrochemical (including FGD)
Applications: heat exchangers, pressure vessels, reactors, strippers, crystallizers, digesters, and polymerizers.
Recommended grades: Ti/CS (cost performance and strength), Ti/SS (cleanliness and temperature resistance), Ti/Ni (dual media / strong acid and alkali).
The titanium layer resists chloride and mixed acid corrosion, while the base plate provides pressure resistance and weldability. Compared with solid titanium, cost is reduced by 40–60% (e.g., Ti/CS).


Electrolysis / electroplating
Applications: cathode plates, conductive beams/bus bars, backplates, and tank linings.
Recommended grades: Ti/Cu (nearly 100% IACS + strong corrosion resistance), Ti/Ni (specific electrolytic media).
The copper core delivers low pressure drop and reduced energy consumption, while the titanium layer resists chlorides, acids, alkalis, and seawater, ensuring fewer shutdowns and longer service life.
Seawater / water treatment / desalination
Applications: condensers, heat exchangers, desalination modules, pump linings, and distribution manifolds.
Recommended grades: Ti/Al (lightweight + high thermal conductivity), Ti/SS, Ti/CS.
The titanium layer resists seawater pitting and crevice corrosion, while aluminum, stainless steel, or carbon steel backplates provide stiffness, cost efficiency, and manufacturability.


Oil & gas / offshore
Applications: pressure vessels, reactors, coke drums, pre-heaters, separators, formed heads, and hydrocrackers.
Recommended grades: Ti/CS, Ti/SS, Ti/Ni.
They resist chloride- and sulfur-containing media. Heads, flanges, and shell sections can be supplied within the same system as plates, reducing weld seams and leakage risk.
Mining / hydrometallurgy (HPAL)
Applications: HPAL autoclaves, flash vessels, chilling units, kettles, crucibles, and digesters.
Recommended grades: Ti/CS, Ti/Ni.
Under high temperature, high pressure, and strong acid stress, the titanium and nickel sides provide separate medium protection, while the base plate ensures pressure resistance and safety redundancy.


Pharmaceutical / food
Applications: reactors, condensers, sanitary pipelines, and shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
Recommended grade: Ti/SS.
The titanium layer offers corrosion resistance and cleanliness, while the stainless steel base provides pressure resistance and easy cleaning, ensuring full compliance with validation requirements.


Architecture / curtain wall / roofing
Applications: curtain wall panels, roofing panels, honeycomb/corrugated cladding.
Recommended grades: Ti/Al, Ti/Zn.
Honeycomb delivers ultra-light weight with high stiffness. The titanium layer ensures weather resistance, while the zinc layer provides anodic protection, combining appearance with long service life.


If you need help selecting the right titanium clad material for your working conditions, please contact our engineering team for a fast solution and quotation within 24 hours.
Advantages of titanium clad materials
- The titanium layer resists seawater, chlorides, and acids/alkalis for long-term durability.
- It maintains oxidation resistance and structural stability even at elevated temperatures.
- Explosive welding plus heat treatment ensures high shear and peel strength, suitable for pressure vessels.
- A thin titanium layer replaces solid titanium structures, reducing cost by 40–60%, with better life cycle cost and less maintenance.
- Titanium can be clad with carbon steel, stainless steel, nickel alloys, aluminum, or zinc to meet diverse operating conditions.
- Plates can be cut (laser/waterjet/plasma), bent, rolled, and welded, with large-size formats supported.
Manufacturing processes
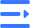
Explosive bonding
Controlled explosives create a high-speed angled collision, forming a solid-state wavy metallurgical bond between the titanium layer and the base plate. The interface is dense and strong.
Contact us now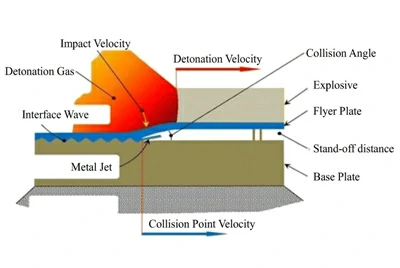
- Instant high-speed solid-state welding forms a wavy bond with high shear/peel strength.
- Base metal structure and chemistry remain unaffected, ensuring machinability and weldability.
- Suitable for large plates, with good heat treatment, leveling, and preforming capability.
We strictly control surface preparation, spacing, and initiation. 100% UT plus shear/peel tests (with optional thickness maps) are performed.
Key equipment can undergo SPWHT simulation re-checks to ensure long-term stability.
Roll bonding (cold/hot rolling)
Through multiple rolling passes (cold or hot), a solid-state pressure weld and metallurgical bond are formed between the cleaned and activated metal surfaces, achieving excellent plate shape and tight tolerances.
Contact us now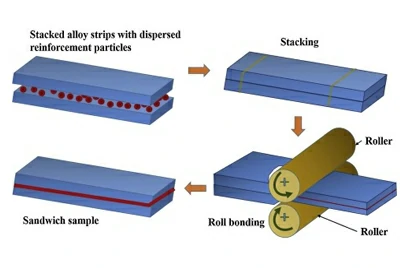
- Multi-pass rolling enables continuous production with good flatness, small thickness tolerance, and high surface quality.
- Suitable for rolling shells and vessels, as well as for stable mass production.
We apply surface activation and cleaning on both the titanium side and the base plate side. After rolling, stress-relief heat treatment and straightening are performed.
UT and shear tests, together with complete dimensional/thickness records, are provided to ensure stable and traceable quality.
Explosive + rolling (combined process)
First, explosive bonding creates a strong and dense interface. Then hot or cold rolling reduces the slab to the target thickness, ensuring both strength and plate flatness.
Contact us now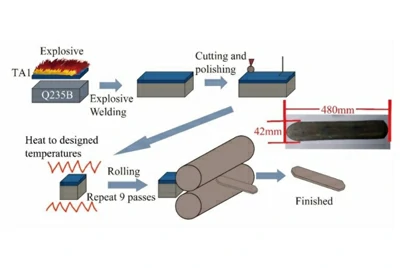
- Explosion bonding forms the slab, followed by hot/cold rolling to final thickness with better consistency.
- Commonly applied in wide plates, long panels, and engineering projects with strict dimensional tolerances.
HIP hot isostatic pressing
Under high temperature and high pressure in an inert atmosphere, atomic diffusion bonding is achieved, resulting in high density and excellent metallurgical continuity.
Contact us now
- Atomic-level diffusion bonding forms under high temperature and pressure, producing a dense interface with superior metallurgical continuity.
- Suitable for aerospace and energy critical components, high-pressure small parts, and transition joints.
We use vacuum encapsulation and degassing, with precise control of temperature and pressure curves. UT, penetration, and microstructural inspections can be added on request.
Common customer risks and our solutions
- Edge corrosion/exposure: Ti edge sealing, end welding, or interference-fit rings prevent exposure in wet zones.
- Thermal cycle cracking: Titanium layer thickness and base grade are recommended based on medium, temperature, and pressure, with strict control of heat input and bending radius.
- Oversize plates: Engineered sectional splicing with full penetration welding and UT, supported by splice drawings and stress evaluation.
- Welding adaptation: WPS/PQR references and weld test blocks provided, with on-site guidance for first-piece welding.
Processing and services
We have extensive experience in manufacturing stainless steel, titanium, nickel, steel, and copper clad materials.
With deep knowledge of application scenarios, we can quickly match the right solution to ensure project success.
- Cutting / leveling / straightening: Ensure dimensional accuracy and straightness, meeting installation requirements for long bus bars and conductive beams in electrolytic cells.
- Machining / drilling / slotting: Use special tools and proper feed rates to avoid tearing the titanium layer; all machining is preferably completed before end sealing.
- End-sealing: After processing, ends are weld-sealed or capped with titanium to fully isolate the copper core, eliminating exposure risks in wet zones.
- Welding services: Ti-to-Ti welding is used in wet zones or at liquid levels, while Cu-to-Cu connections are arranged in dry zones, ensuring long service life and low contact resistance.




Simply send us your drawings or application parameters, and we will provide integrated processing, welding, and quality inspection services.
The products are delivered ready-to-use, with no secondary treatment required.
Quality control & testing
We strictly follow international and national standards (GB/T, ASTM, etc.) to ensure titanium clad copper products meet requirements for conductivity, corrosion resistance, and structural strength. Main inspections include:
- Bending test: 90° bending per GB/T 232, ASTM E190, verifying no delamination or cracking.
- Metallographic analysis: Optical microscope per GB/T 6394, ASTM E112, checking bond quality and grain size.
- Cupping test: GB/T 4156, evaluating material ductility.
- Chemical analysis: Oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen testing per GB/T 4698, ASTM E1409/E1447, ensuring raw material purity.
- Ultrasonic testing (UT): GB/T 12969.2, 100% inspection for interface delamination and internal defects.
- Dimensional check: Optical measuring instruments for precise tolerance control.
- Leak test: ASTM B338, ensuring tubes are free from leakage defects.
- Mechanical test: Universal testing machine per GB/T 228, ASTM E8, measuring tensile strength and elongation.
- Hardness test: Vickers hardness per GB/T 4340, ASTM E384.
We operate advanced production and testing equipment for titanium clad copper, covering the entire process from billet preparation and precision machining to final inspection.




We not only operate a complete production line but also integrate testing, processing, and quality control.
This allows us to deliver finished parts that are fully certified and ready to use, ensuring your project passes audits smoothly and runs reliably over the long term.
Our services
- Quality assurance: Explosive welding + hot rolling process, high strength, compliant with ASTM/ASME/NB/T. UT, shear tests, and 3.1/3.2 certificates provided on delivery.
- Customization: Full customization of plates, tube sheets, heads, flanges, and more, with flexible size, thickness, and material options.
- Technical support: Process solutions, welding guidance, corrosion data, and case studies to support bidding and project execution.
- Delivery advantage: Scaled production lowers cost and lead time, with fast quotation and flexible payment terms.
- Packaging & shipping: Export-grade packing (waterproof paper + wooden pallets + steel bands), clear labeling, and full transport protection.
- Payment terms: Flexible options including T/T, L/C, and D/P.
- Inspection services: Witnessing available for materials, welding, NDT, finished products, and packaging.
- Global communication: Multi-language documentation and localized support for smooth procurement and worry-free after-sales service.
Related clad metal products
In addition to the titanium clad series, we also provide a variety of other clad metal materials to meet different working conditions and budget needs:

Nickel Clad Steel

Aluminum Clad Copper

Aluminum Clad Steel

Copper Clad Steel

Zirconium Clad Steel

Stainless Clad Steel
With one-stop sourcing and solutions tailored to your application, we deliver fast material selection and quotation within 24 hours — making your procurement easier and more efficient.
FAQ — Titanium Clad
What is titanium clad?
Titanium clad is a composite material that bonds titanium with carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, or nickel, combining titanium's corrosion resistance with the base metal's strength and cost efficiency.
What are the downsides of titanium cookware?
Pure titanium cookware is expensive and has average thermal conductivity. Titanium clad designs are often used to balance performance and cost.
What is the downside of titanium?
Pure titanium is costly and difficult to process, while titanium clad saves 40–60% in cost and still maintains corrosion resistance.
Is titanium cookware better than stainless?
Titanium is lighter and more corrosion resistant, while stainless steel is more economical and wear resistant. Clad designs combine the advantages of both.
How much does titanium cost?
Solid titanium is expensive, but titanium clad significantly reduces cost while ensuring long service life, offering better life cycle cost.
What is the typical thickness of the titanium layer in clad plates?
Currently, 2.5–3.5 mm is common. In highly corrosive or high-erosion environments, it can be increased to 6–8 mm.
This standard has evolved since the 1960s from an initial 2 mm, balancing cost, corrosion life, and repairability.