Titanium–Steel Clad Plate
Updated : Sep. 24, 2025Titanium-steel clad plates are constructed with a carbon steel/low-alloy steel base layer coated with titanium or titanium alloys, metallurgically bonded through explosive cladding or rolling. They combine the corrosion resistance of titanium with the strength and cost-effectiveness of steel, making them an ideal material for equipment in industries such as chemical processing, desalination, and energy.
- Corrosion Resistance: The titanium layer resists pitting, crevice corrosion, and erosion, with a lifespan far exceeding that of stainless steel and duplex steel.
- Cost Control: The steel base provides strength and rigidity, resulting in a significantly lower lifecycle cost than pure titanium solutions.
- Quality Traceability: 100% UT/Shearing/Bending/Spark Leak Testing process records are available, with third-party reports available.
- Worry-Free Delivery: Technical review → Quick quote → Prototyping → Third-party inspection → Factory delivery, standardized process.
Chalco Titanium strictly adheres to ASTM B898, GB/T 8547, GB/T 8546, and NB/T 47002.3 standards. Its primary process is explosive cladding, supplemented by rolling cladding/HIP. Complete quality inspection documentation and expedited delivery options are provided to ensure project acceptance and implementation.
Specifications of Titanium Steel Composite Plates
| Base layer | Material | Q345R,16MnR,SA516 Gr.70,A516,A515,A266,A572,A709 |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 5 – 110 mm | |
| Coating | Material | Gr2,Gr7(Ti+Pd),Gr12(Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni) |
| Thickness | 0.5 – 10 mm (conventional 1 – 3 mm) | |
| Total thickness | 6 – 120 mm, customizable | |
| Maximum size Tolerance | Width | ≤ 3000 mm |
| Length | ≤ 12000 mm | |
| Tubesheet Diameter | φ4000 mm | |
| Maximum size | Flatness | 0.5 – 0.8 mm/m |
| Surface Roughness | Polished ≤ Ra 1.0 μm; Pickled ≤ Ra 4.5 μm | |
| Thickness Tolerance | Titanium layer: ±0.2 mm; Total thickness: ±5% | |
| Composite process | Primarily explosive lamination, combined with heat treatment/hot rolling and leveling; roll lamination or HIP is also supported. | |
| Processing capability | The machine can process tube sheets, support drilling, surface finishing, flatness and hole position accuracy control; and implement spark leak detection/airtightness leak detection on key surfaces. | |
| Surface condition | Acid-washed, polished, and machined surfaces are available; titanium surfaces can be protected with film. | |
| Standard | ASTM B898,GB/T 8547,GB/T 8546,NB/T 47002.3 | |
Contact us for a customized titanium steel composite plate solution and a quick quote. Chalco Titanium can make your project more worry-free and reliable.
Titanium-Steel Clad Plate Product Categories
Titanium-Steel Clad Plate
Base: Pressure vessel steels such as Q345R, 16MnR, SA516 Gr.70
Clad: Gr1, Gr2, Gr7, Gr12
Dimensions: Thickness Range Total 6–120 mm; Ti layer 0.5–10 mm (typ. 1–3 mm); Width ≤ 3000 mm
Applications: Columns, storage tanks, reactors, evaporators, etc.


Titanium Clad Tube Sheet
Base: 16MnR, SA516 Gr.70, A516
Clad: Gr2, Gr7, Gr12
Dimensions: Thickness Total 20–150 mm; Ti layer ≥ 1.0 mm; Diameter ≤ φ4000 mm
Machining Precision: Drilling/surface finishing; spark & airtightness testing
Titanium-Steel Clad Head/Plate
Base: Q345R, SA516 Gr.70
Clad: Gr2, Gr12
Dimensions: Thickness Total 8–100 mm; Ti layer 1–3 mm; Coil Dia ≤ 4000 mm; Head Dia ≤ 6000 mm
Applications: Pressure vessel shells, end caps

To select the appropriate titanium-steel clad plate type, simply send us your design parameters (base material, titanium layer, thickness, and dimensions). Chalco Titanium will provide you with a professional quote and technical solution within 48 hours.
Typical Applications of Titanium-Steel Clad Plates
Chemical Industry / Salt Chemical Industry / Chlor-Alkali
Long-term operation of equipment with chlorine-containing, highly oxidizing media can easily lead to cracks and stagnant areas forming on flange and lining surfaces, increasing the risk of pitting corrosion and leakage.
Titanium-steel clad plates balance longevity and cost with a titanium layer directly facing the media and a steel base for pressure bearing and manufacturability.
They are used in reactors, absorption/distillation towers, tank linings, and shell-and-tube heat exchangers, ensuring long-term operation through standardized welding and leak detection procedures.
Gr7/Gr12 is recommended for key areas to improve resistance to pitting corrosion and cracking. UT and leak detection records should be maintained at the factory and upon delivery.
Base Material: SA516 Gr.70 / Q345R / 16MnR
Cladding Material: Gr7 (Chloride-Resistant Pitting) / Gr12 (Crevice and Erosion) / Gr2 (General Purpose)
Inspection/Processing: UT 100% (according to agreed grade), PT (Titanium Surface), Spark/Airtight Leak Testing; Edge Stripping → Steel-Base Load Welding → Titanium Layer GTAW Sealing
Specifications: ASTM B898 / NB/T 47002.3

Desalination / Offshore
The combination of high Cl⁻ levels and high flow rates in seawater results in high costs for continuous equipment operation and downtime.
Tubesheets and gaskets are particularly susceptible to erosion and crevice failure.
Titanium-steel clad plates achieve a balance of "corrosion resistance = pure titanium, structure = steel base" in MED/MSF/RO sections and seawater cooling systems.
Gr7/Gr12 plates are used in key areas to enhance pitting, crevice, and erosion resistance, while also controlling surface roughness and leak detection accuracy.
Base Material: SA516 Gr.70 / 16MnR
Clad Material: Gr7 / Gr12 (Preferred for high flow rates/chlorine-containing conditions)
Inspection/Processing: 100% spark testing/airtightness testing on tube sheet ends; full UT coverage; flatness and hole position accuracy specified on drawings
Specifications: ASTM B898 / NB/T 47002.3

Power/FGD Chimney Lining
Cold-end condensate acid corrosion and thermal cycling coexist, requiring long-term, stable corrosion protection at the joints between the lining and the plate.
Titanium-steel clad plates are used for condenser plates, steam generator components, and FGD chimney linings, providing stable corrosion resistance while maintaining pressure and plate forming.
After forming, repeated UT and PT testing of critical interfaces are performed to reduce leakage and maintenance during operation.
Base Material: SA516 Gr.70 / Q345R
Clad Material: Gr2 (General Purpose) / Gr12 (More Stable in Condensing Acid Environments)
Inspection/Processing: Large plates with fewer seams; UT re-inspection after forming, PT/leak testing at interfaces
Specifications: ASTM B898 / NB/T 47002.3; Chimney Linings Refer to DL/T 1590


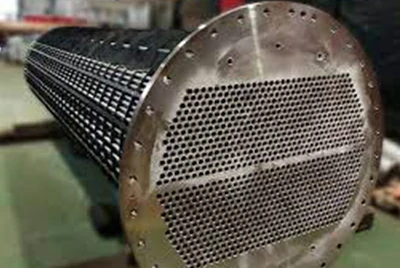
Heat Exchanger Tubesheets
Densely punctured, with significant gaps and stagnation, are among the most vulnerable areas to failure.
Titanium-steel composite tubesheets significantly extend maintenance cycles through precise control of flatness and hole position accuracy, end-face spark/airtightness testing, and titanium layer sealing welding.
Material matching and assembly schedule with the tube/shell are recommended to be reviewed during the design phase.
Base Material: 16MnR / SA516 Gr.70
Clad Material: Gr2 / Gr7 / Gr12 (selectable based on media and flow rate)
Inspection/Processing: 100% end-face spark testing for leaks and airtightness; flatness and hole position accuracy controlled according to drawings; GTAW seal welding and backside protection
Titanium Steel Composite Plate vs Pure Titanium Plate vs Stainless Steel Plate
| Dimensions | Titanium–Steel Clad | Pure Titanium | Stainless steel (304/316L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | The titanium layer directly contacts the medium, offering corrosion resistance comparable to pure titanium (more stable in seawater, chlorine-containing media, and strong oxidizing agents). | Strongest | Susceptible to pitting and crevice corrosion in seawater and chlorine-containing media |
| Strength/Manufacturing | The steel base provides strength and weldability, making it easy to roll and form, and highly compatible with equipment specifications. | Lower strength, high thickness/support requirements, narrow manufacturing window | Process-friendly |
| Investment Cost | Significantly lower than pure titanium (typically saving 30–50%). | Tallest | Minimum initial wear |
| Lifespan/Downtime | Almost pure titanium, far exceeding stainless steel; low downtime. | Longest | Short lifespan, frequent maintenance |
| Applications | Suitable for seawater, chlorine-containing media, strong oxidizing agents, heat exchanger tube sheets, and pressure vessel shells. | Extremely corrosion-resistant, extremely costly downtime, and budget-friendly | General use in non-chlorine-containing neutral media, low corrosion risk |
- Budget vs. Lifespan: If you have a limited budget but require a lifespan close to that of pure titanium, choose titanium-steel clad plate. If you have a generous budget and require extreme lifespan, choose pure titanium.
- Media and Risk: For seawater, chlorine-containing, highly oxidizing media, or where cracks are unavoidable, titanium-steel clad plate (Gr7/Gr12) is preferred. For low-corrosive neutral media, stainless steel is sufficient.
- Downtime Window: If you want minimal downtime but high cost, titanium-steel clad plate or pure titanium are options. If periodic maintenance is acceptable, stainless steel may still be considered.
- Structure and Specification: If you require large-scale coiling, pressure bearing, or ASME vessel systems, titanium-steel clad plate is the most suitable option.
Manufacturing & Processing
Chalco Titanium integrates its entire process from "complex processing capabilities → processing capabilities → quality and delivery." We can manufacture large-sized plates and tube sheets, as well as machine and assemble interface components according to drawings, ensuring complete engineering from materials to equipment components.
Process Routes Explosive Bonding (mainstay): Large plates are formed in one go, providing strong metallurgical bonds; subsequent heat treatment/hot rolling and flattening can be used to optimize plate shape.
Roll-Bonding: Tighter thickness and plate shape control, suitable for parts sensitive to flatness and tolerances.
HIP (Hot Isostatic Pressing): A supplementary route for high-end customization and specialized structural parts (implemented after review).
Supply Capacity Total Thickness: Approximately 6–120 mm (Thicker thicknesses available upon request) | Titanium Layer: 0.5–10+ mm (typically 1–3 mm)
Dimensions: ≤ 3000 mm (width) × ≤ 12000 mm (length) | Tubesheet Diameter ≤ φ4000 mm
Typical Materials: Base Material: Q345R/16MnR/SA516-70; Cladding: Gr2/Gr7/Gr12 (selected based on application conditions)
Processing Capabilities Cutting and Forming: CNC plasma/water jet cutting, tube coiling, hot pressing/cold spinning of heads, leveling and shaping
Machining: Tube sheet drilling, countersinking/tapping, and surface finishing; flatness and hole position accuracy are controlled according to the drawing
Edge Processing: Delamination → Steel base load welding (SMAW/GMAW/SAW) → Titanium layer GTAW Sealing welding, backside protection, and welding procedure guidance (WPS/PQR) are provided.
Quality and Inspection (Third-Party Witness Available: TÜV/SGS) 100% UT (performed according to the agreed class, default inspection on the titanium surface), PT (titanium surface), spark/air leak testing (tube sheet/end face)
Shear/bend re-inspection; projects involving post-weld heat treatment (SPWHT) re-inspection is available.
Dimensions/Appearance: Thickness tolerance (titanium layer ±0.2 mm, total thickness ±5% or as per standard/contract agreement), plate shape/flatness, surface roughness (polished ≤ Ra 1.0 μm, pickled ≤ Ra 4.5 μm)
Traceability: Material certification (titanium/steel), composite and heat treatment records, NDT/mechanical reports, marking and coding
Delivery and Documentation ITP (Inspection Plan) templates, packing lists, and protective packaging (film/oil seals for titanium surfaces, rust protection and reinforcement for steel surfaces) are provided.
Quick quotes and expedited delivery options are available. We have extensive experience in factory delivery and support for compliant documentation for overseas projects.
FAQ
How do I choose the thickness of the titanium layer?
The thickness depends on the medium (chlorine content/oxidizing properties), temperature and flow rate, the presence of cracks/stagnation, design life, and leak detection strategy. Conventional thicknesses are 1.0/2.0/3.0 mm; for seawater/chlorine-containing or high-flow areas, thicker thicknesses or Gr7/Gr12 are preferred. For high-risk areas such as heat exchanger tube sheets and flange ends, a higher thickness and 100% leak detection are recommended.
How do I combine the steel base with the titanium layer?
Common combinations: SA516-70/Q345R/16MnR + Gr2 (general purpose); for chlorine-containing/crack-sensitive applications: SA516-70/Q345R + Gr7 (Pd-modified) or Gr12 (Ti-0.3Mo-0.8Ni). Choose the right thickness based on the medium, temperature and pressure, and lifespan.
How do I choose between explosive cladding, rolling cladding, and HIP?
Explosive cladding (mainstream): Large size, high cost-effectiveness, with heat treatment/flattening for controllable plate shape.
Rolling cladding: Prioritized for workpieces with tighter plate shape/tolerances.
HIP: Approved for special structures and high-end customization applications after evaluation.
All three methods are metallurgical and should be selected based on project specifications and budget.
What is the correct approach for edge welding and sealing?
Follow the "edge peeling → steel-based load-bearing welding (SMAW/GMAW/SAW) → titanium layer GTAW sealing welding" procedure. Backside protection should be implemented to prevent high-temperature titanium inhalation. Transition joints can be used to connect dissimilar materials. Spark/airtightness testing is mandatory on heat exchanger end faces.
How should testing and standards be written in the contract?
It is recommended to cite ASTM B898 / NB/T 47002.3 and specify: UT 100% grade (B898 Class A/B/C; if unspecified, Class B is generally used, tested from the titanium surface), shear strength threshold (B898 baseline ≥20,000 psi ≈ 138 MPa), bend/PT (titanium surface)/spark leak detection (tubesheet), dimensional and appearance tolerances, batch size, and sampling frequency.
Is SPWHT required? If so, what needs to be retested?
If the pressure vessel undergoes a post-weld heat treatment (PSHT) process, SPWHT (simulated PWHT) is recommended. After SPWHT, retest shear strength and UT, and perform additional bend/PT if necessary to ensure interface stability.
What is the typical scope of supply?
Total thickness 6–120 mm; titanium layer 0.5–10+ mm (conventional 1–3 mm); width ≤ 3000 mm, length ≤ 12000 mm; tubesheet diameter ≤ Ø4000 mm. Customization is possible according to drawings and is subject to contract.
What parameters are required for ordering/inquiry?
Base steel grade and thickness, titanium layer grade and thickness, total thickness and plate dimensions, UT grade, whether spark/hermetic leak testing is performed, quantity and delivery time, media and temperature, pressure/flow rate, and drawings (including hole location, flatness, and roughness requirements).
Titanium-steel clad plate vs. pure titanium/stainless steel: How to quickly decide?
Limited budget but requiring a lifespan close to pure titanium → Titanium-steel clad plate; Extreme corrosion resistance and ample budget → Pure titanium; Neutral/low corrosion with acceptable maintenance cycles → Stainless steel. Titanium-steel clad plate (Gr7/Gr12) is preferred when working with chlorine, seawater, or strong oxidation, or when cracks are unavoidable.
Can you provide machining and factory delivery?
Yes. We support coiling/heading, tube sheet drilling and surface processing, edge stripping and seal welding, and other advanced processing. We also provide ITP templates, third-party inspection (TÜV/SGS), complete quality inspection files, and protective packaging. Factory delivery is available, and expedited delivery is also possible.