Titanium Flanges
Updated : Jun. 23, 2025Quick Navigation: Titanium Flange Types
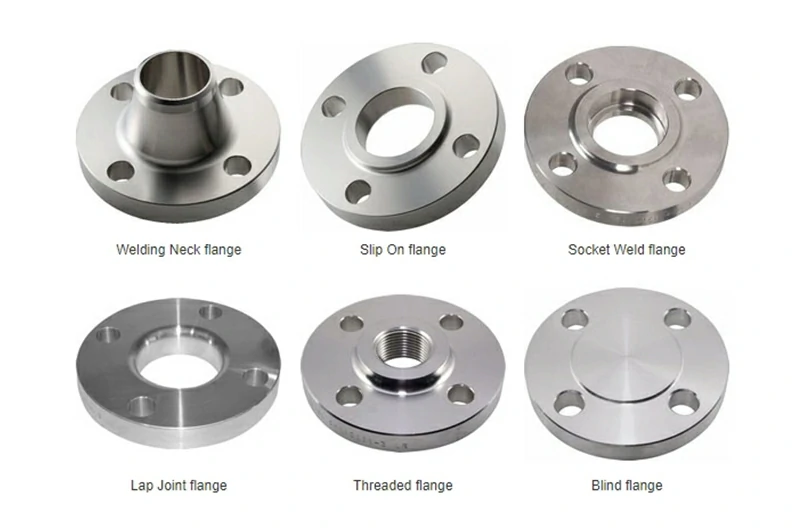
| Flange Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Blind Flange | Seals the end of pipelines or inspection ports |
| Weld Neck Flange | Long neck for stress transfer in high-pressure systems |
| Slip-On Flange | Easy-to-install design for medium/low pressure |
| Threaded Flange | Threaded connection for non-welded systems |
| Socket Weld Flange | Smooth bore for high purity and small-diameter use |
| Lap Joint Flange | Paired with stub ends, ideal for lined systems |
Titanium Blind Flange

Blind flanges are designed to seal the end of pipelines or inspection ports. They can bear the full design pressure of the pipeline. The flange body has no borehole and may have reinforcements on the back when needed.
Common sealing faces include RF, RTJ, and FF. When the pressure rating exceeds Class 900 or the medium contains a high concentration of chloride ions, RTJ provides more reliable sealing.
Available alloys include GR1 and GR2. For higher strength or temperature resistance, GR5 is an option. In strong chloride environments, palladium-containing GR7 is often used.
Dimensions and pressure ratings follow ASME B16.5 Class 150–2500 (NPS ½–24), ASME B16.47 Series A/B (NPS 26–60), EN 1092-1 PN10–40, or GB/T 9119 PN2.5–40.
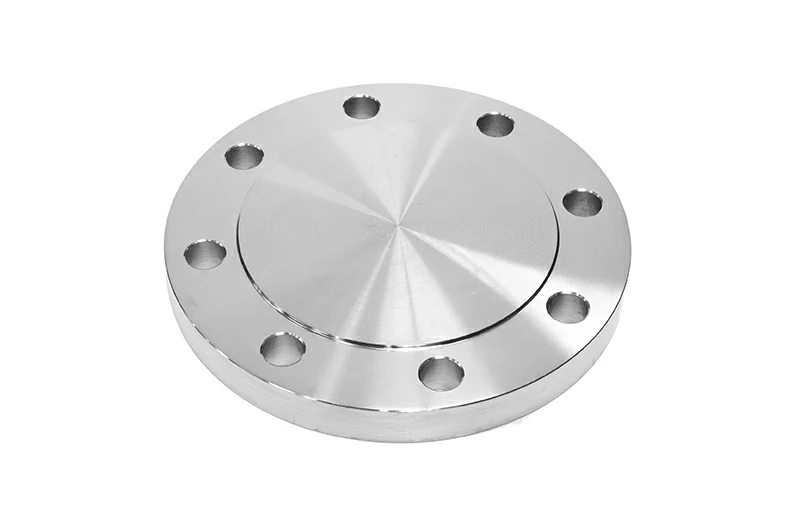
Titanium Weld Neck Flange (Butt Weld Flange)

Weld neck flanges have a long tapered neck welded to the pipe. This design smoothly transfers stress to the pipe wall. They perform best in high-pressure, high-temperature, and frequent thermal cycling systems.
Sealing faces include RF and RTJ. RTJ is typically recommended when pressure is above Class 600.
For standard pressure, GR2 is commonly used. For high pressure or temperatures from −196°C to 400°C, GR5 is suitable. For chloride or reductive acid environments, GR7 is an option.
Manufactured to ASME B16.5 Class 150–2500 (NPS ½–24), EN 1092-1 PN10–100 (DN10–600), and HG/T 20592 PN2.5–100 (DN15–600) standards.
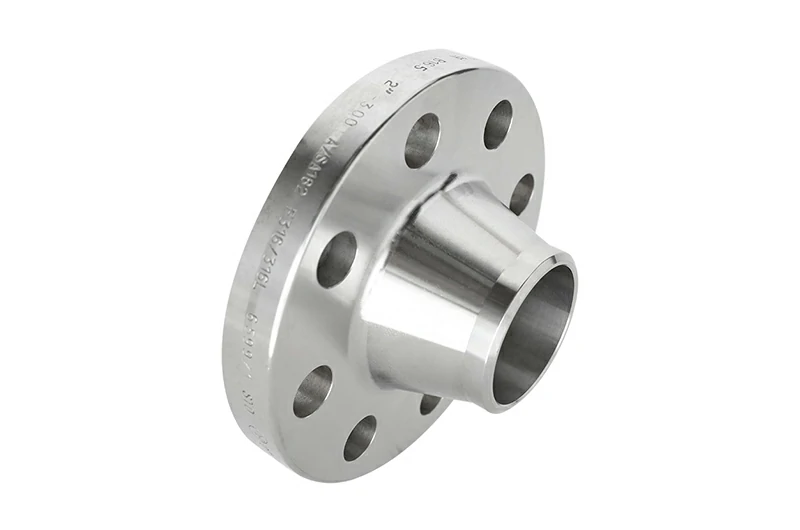
Titanium Slip-On Flange

Slip-on flanges are installed by sliding the pipe through the flange bore and welding on both sides. They are easy to position and have a lower initial cost. Thus, they are common in medium- and low-pressure systems.
Due to structural rigidity limits, they are generally not recommended for Class 600 or higher, or in conditions with strong pulsating loads.
Available alloys include GR1 and GR2. For media with high chloride ion content, GR7 is recommended.
Specifications cover ASME B16.5 Class 150–600 (NPS ½–24), EN 1092-1 PN10–40 (DN15–600), and GB/T 9119 PN2.5–25 (DN15–600).
Titanium Threaded Flange
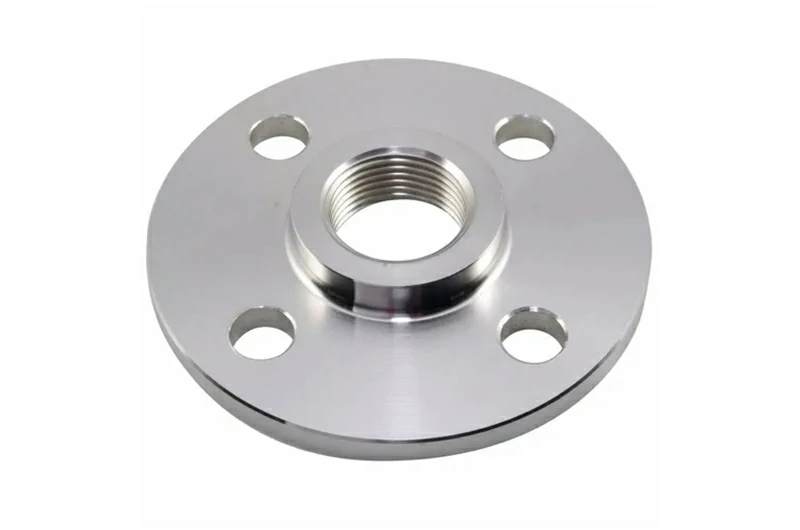

Threaded flanges connect to pipes via internal threads, eliminating the need for welding. They are ideal for low-pressure, small-diameter systems or flammable environments where welding is not feasible.
Available sealing faces include RF and FF. While not suited for high pressure, they offer quick installation and easy maintenance.
Supplied in GR2 and GR5 titanium. For chloride-rich media, GR7 is recommended.
Standard sizes cover ASME B16.5 Class 150–600 (NPS ½–4) and EN 1092-1 PN10–40 (DN15–100).
Titanium Socket Weld Flange
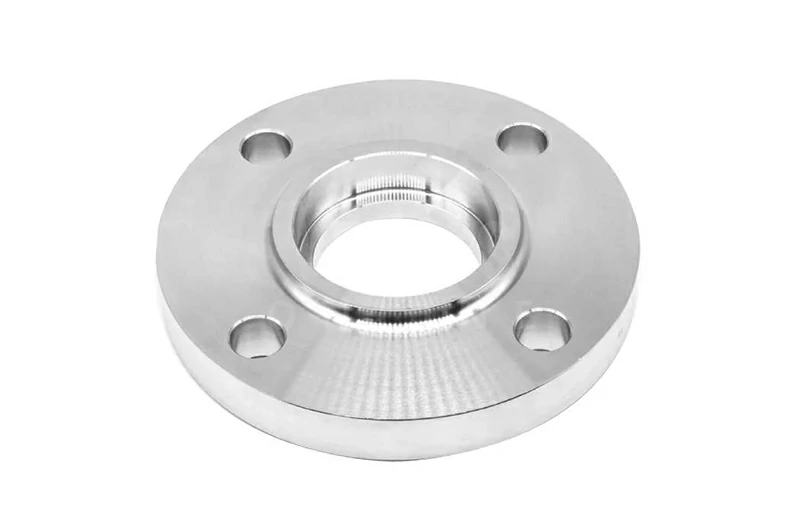

Socket weld flanges have a recessed area inside the flange. The pipe is inserted and then welded from the outside with a fillet weld. The inner wall is smooth and continuous, reducing turbulence and sediment.
They are mainly used for small diameters (NPS ½–4) and pressure classes from 150 to 1500. Typical applications include instrumentation pipelines or systems handling high purity media.
Materials are usually GR2, with options for GR5 or GR7 depending on conditions.
Manufactured according to ASME B16.5 Class 150–1500, HG/T 20592 PN2.5–100 (DN15–100), or EN 1092-1 PN10–63 (DN15–100).
Titanium Lap Joint Flange
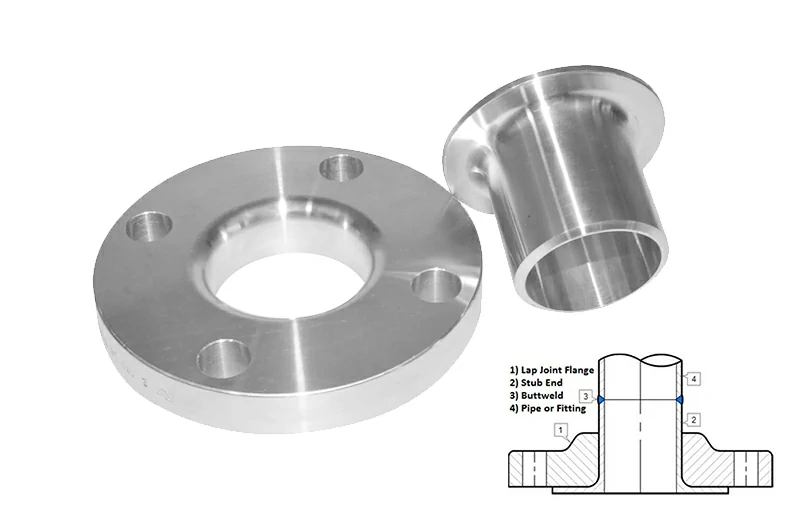
Lap joint flanges must be used with stub ends or flanged pipe segments. The flange body does not contact the medium directly. This design allows easy installation and alignment. It is also suitable for lined or composite pipelines.
Common flange material is GR2. For higher strength, GR5 can be used.
Sizes include ASME B16.5 Class 150–600 (NPS ½–24) and EN 1092-1 PN10–40 (DN15–600), meeting most needs for corrosion resistance or frequent disassembly.
How to Select the Right Titanium Flange
Choosing a suitable titanium flange not only affects the sealing and stability of the system, but also affects the long-term operating safety and maintenance costs.

Pressure and Temperature Requirements
When selecting a titanium flange, it must be able to withstand the system's maximum operating pressure and temperature.
Class 150 flanges are typically suitable for systems up to 285 psi (approx. 2 MPa) and 300°F (approx. 150°C).
Class 600 flanges can handle up to 1500 psi (approx. 10 MPa), making them suitable for higher-temperature environments
For extreme conditions such as cryogenic applications (−196°C, e.g., liquid nitrogen) or high-temperature steam systems (up to 400°C), GR5 titanium with a weld neck design is recommended to ensure long-term sealing and structural integrity.
Size and Standard Compatibility
The flange must match the pipeline's size and standard (e.g., ASME, EN, JIS, GB), including bolt hole layout, face height, and thickness, to ensure proper fit and minimize stress concentrations.
Material and Corrosion Resistance
Choose the titanium grade based on the fluid type. GR2 is a general-purpose corrosion-resistant alloy. GR5 is ideal for high-pressure applications requiring strength, while GR7 offers superior resistance in chloride-rich or acidic environments.
Sealing Face and Gasket Matching
Sealing performance depends on the face type (RF, FF, RTJ) and its compatibility with the selected gasket. RTJ is recommended for high-pressure systems with metal ring gaskets, while RF is widely used in medium to low pressure with spiral wound or non-metal gaskets.
Installation Conditions and Connection Method
If hot work is restricted on site or quick disassembly is needed, threaded flanges are preferred. For systems with vibration or harsh long-term operation, weld neck flanges are ideal due to their strength and stress-distributing structure.
Purchasing and Service Guide
- Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Starts from 1 piece; common sizes have 30 pcs in stock
- Delivery Time: Stock items ship within 3 days; custom forgings take 15–25 days
- Shipping: Small packages via DHL/UPS air freight; large items shipped by sea in ISPM15 wooden crates
- Payment Terms: T/T 30% deposit, 70% balance upon copy of bill of lading; L/C accepted
Need Titanium Flanges?
- Chat on WhatsApp: +86-173-44894490
- Email Us: contact@chalcoaluminum.com
Get Your Price in Minutes!