Titanium vs Platinum
Updated : Sep. 22, 2025Titanium and platinum are both metal materials widely used in industry, but they differ significantly in density, strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, conductivity, processability, and application directions.
Titanium is known for its light weight, high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, and is the main structural material; while platinum is widely used in electrochemistry, catalysis and high-temperature precision components due to its chemical inertness, stability and rare value.
Analyze the differences between titanium and platinum from multiple perspectives, including material properties, processing technology, and typical applications, to help you make more accurate judgments in material selection decisions.
Density and weight difference
Titanium has a density of approximately 4.51 g/cm³, while platinum has a density of 21.45 g/cm³, almost five times that of titanium. Titanium is more suitable for applications requiring lightweighting, such as aviation and sports equipment. Platinum, due to its higher density, is often used in applications requiring high stability, such as high-temperature smelting and high-pressure catalysis.
Strength and hardness comparison
Titanium is significantly stronger than platinum. For example, Grade 5 titanium alloy has a tensile strength of 895 MPa and a Vickers hardness of 830–1000 HV, compared to platinum's 125–220 MPa and 56–60 HV. Titanium is suitable for high-strength structural parts, while platinum is primarily used for flexible or electrochemical functional components.
Chemical stability and corrosion resistance
Platinum has extremely high chemical stability and can withstand strong acids and oxidants such as aqua regia and concentrated nitric acid. It is often used in corrosive environments such as electrodes and electrolytic cells. Titanium relies on the surface The TiO₂ passivation film provides protection and good corrosion resistance in seawater and chlorides, but may still be damaged in strong acids such as hydrofluoric acid.
Thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity
If the application requires high thermal or electrical conductivity, platinum is a better choice. Its thermal conductivity is 71.6 W/m·K and its electrical conductivity is 9.43 MS/m. Titanium, on the other hand, has a thermal conductivity of only 21.9 W/m·K and an even lower electrical conductivity of 2.38 MS/m. This makes platinum more suitable for applications such as electrical contacts, electrodes, and heating elements.
Surface characteristics and appearance style
Platinum has a naturally silvery white color with a noble luster, requiring no electroplating or anodizing. Titanium, on the other hand, has a naturally grayish hue, but it can be anodized to create colors such as blue, purple, gold, and rainbow, making it suitable for customization and visual design. Titanium's surface is difficult to polish, making it suitable for matte/industrial applications. Platinum, on the other hand, is highly ductile and lends itself to mirror finishes.
Processing difficulty and formability
Titanium is difficult to machine, requiring specialized tools, protective atmosphere welding, and heat treatment. Its low machinability stems primarily from its high hardness and low thermal conductivity. Platinum, on the other hand, is highly formable and suitable for a variety of manufacturing processes, including cold rolling, stamping, welding, and laser processing. Platinum offers advantages for micron-scale parts and electrode manufacturing, while titanium is preferred for large structural components.

Application scenario
Although titanium and platinum are far apart on the periodic table, they are both widely used in the field of high-performance materials. However, their application focuses and typical uses are significantly different.
Industrial and structural applications
- Titanium, with its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, is widely used in aerospace (fuselage skins, landing gear), marine engineering (ship structures, submarine pipelines), and chemical equipment (heat exchangers, pressure vessels). Its low density and excellent mechanical properties make it a preferred lightweight, high-strength structural material.
- Due to its high melting point and strong chemical inertness, platinum is primarily used in industry for high-temperature components (crucibles, electrodes), glassmaking, laboratory equipment, and sensors for special environments (such as Pt100 thermal resistors). While it's not suitable for structural components, it's indispensable in precision high-temperature control applications.


Electrochemistry and energy fields
- Titanium is commonly used as the anode substrate and, after surface coating (such as iridium coating or platinum coating), is used in electrolytic water treatment, the chlor-alkali industry, and wastewater treatment. It has strong resistance to chloride corrosion and is suitable for long-term stable operation.
- Due to its strong electrocatalytic activity, platinum is a core electrode material for fuel cells, water electrolysis to produce hydrogen, and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). It is also one of the preferred precious metal anodes, and despite its high cost, its performance is irreplaceable.
Medical and biological applications
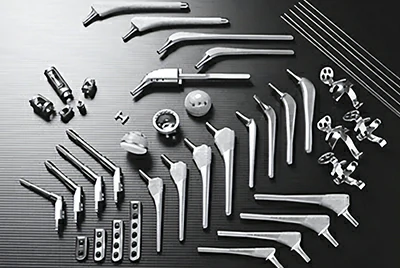
- Titanium, with its excellent biocompatibility and non-toxicity, is a common material for long-term implants such as artificial joints, fracture fixators, and dental implants. In particular, Ti-6Al-4V ELI (low-clearance version), which complies with ASTM F136 standards, is widely used in orthopedics.
- Platinum is often used in places with extremely high requirements for conductivity and stability, such as pacemaker electrodes, nerve stimulation electrodes, and cancer treatment injection needles, because of its corrosion resistance, plasticity, and non-magnetism.

Jewelry and high-end consumer goods
- Titanium, due to its lightness, strength, and ability to be anodized, is used in modern jewelry, watch cases, and fashionable wedding rings, ideal for those seeking a technologically advanced look and personalized customization. Its scratch resistance makes it suitable for everyday wear, but the ring size cannot be adjusted.
- Platinum is a traditional symbol of high-end jewelry. Its natural white gold luster, exceptional density, and rarity make it the metal of choice for high-end wedding rings and luxury jewelry. Its ease of manufacture, comfort, and lifelong maintenance and adjustment make it a symbol of permanence and elegance.
Choose Chalco Titanium for a comprehensive titanium solution
As a professional titanium production and export company, Chalco Titanium is committed to providing global customers with titanium products and customized solutions with excellent performance, complete specifications and flexible delivery.
We can supply the following titanium products on a long-term basis