Lightweight High-Strength Corrosion-Resistant Titanium Rivets
Titanium rivets give you aerospace strength, 45 % weight-saving over steel, and 200 °C heat resistance where aluminum quits—plus zero galvanic corrosion on composites.
Why choose titanium rivets?
Titanium offers four major advantages: easy fabrication, lightweight, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance.
- Grade 2 and Ti-5Al-2.5Sn α-titanium alloys can be cold-riveted at room temperature, reducing rework and tooling costs.
- With a density of only 4.51 g/cm³—45 % lighter than steel—titanium rivets significantly cut structural weight, favored by aerospace and carbon bicycle manufacturers.
- Its natural oxide film ensures "zero red rust” even after 1 000 hours of salt-spray testing, extending maintenance intervals.
- Grade 5 maintains about 900 MPa tensile strength at 400 °C, making it ideal for exhaust systems and other hot-end parts.
Titanium rivets solve three challenges in one go—weight, lifespan, and maintenance cost—helping your projects stay light, strong, and worry-free.
Titanium rivets product types

Titanium blind rivets
These allow high-strength fastening from one side, making them the top choice for ship decks, carbon frames, and on-site repairs.
Contact us now
- Stocked in Ø 3.2 / 4.0 / 4.8 mm dome head and large flange sizes, with Grade 2 titanium blind rivets in 3/16 inch leading sales.
- Shear and tensile strength are verified after 1 000 h salt-spray testing, and sealed versions pass both waterproof and airtight tests.
- Lock-mandrel design ensures ≤ 1 % mandrel loss.
- All models are compatible with ≥ 12 kN rivet guns, supplied with a complete selection chart and free samples.
Titanium solid rivet
Deliver ≥ 900 MPa shear strength for aircraft skins, primary beams, and pressure vessels.
Contact us now
- Stock covers Ø 1.6–12 mm in 100° countersunk and round head designs (MS20426 / MS20470 / aerospace titanium solid rivet series).
- Each shipment includes a CoC and AMS shear/tensile reports, with matching bucking bars and pressure setting guides.
- A direct replacement for aluminum rivets, they add almost no extra weight yet multiply corrosion life, making them the most cost-effective choice for long-term operations.
Titanium self-piercing rivet
Engineered for "no-drill” joining of dissimilar materials such as aluminum and steel, Ø 3–6 mm dome head rivets pierce and lock in a single press stroke.
Contact us now
- Tip hardness and 2 × 10⁶ cycle fatigue curve data are published to eliminate concerns over hybrid material durability.
- SPR press tooling parameters and small-batch sample runs are available to help you quickly validate process feasibility.
Titanium split rivet
Sharp-point split tails easily penetrate wood, plastic, and leather, with Ø 2.4–4.8 mm among the best sellers.
Contact us now
- Optimized tooth design ensures even leg expansion, supplied with a quick-reference chart for minimum edge distance and maximum grip thickness.
- Sample-to-site trials are supported to prevent cracks or poor holding in soft materials.
Titanium hollow rivet / cherry rivet
An ideal solution for light-load fastening and pivot joints, commonly in Ø 2–5 mm dome head designs.
Contact us now
- Grade 2's high ductility ensures crack-free flaring, with tube wall thickness and axial load data fully transparent.
- Optional laser marking or anodized colors offer both traceability and visual appeal.
Titanium flush rivet
The 100° / 120° countersunk design keeps high-speed aerodynamic surfaces perfectly smooth.
Contact us now
Best-selling Ø 1.6–8 mm titanium flush rivet 100 degree models feature flatness ≤ 0.05 mm and surface roughness ≤ Ra 0.8 µm, proven through fatigue and paint-peel testing.
Each set includes a quick-reference chart for hole diameter and countersink depth to ensure first-time installation success. Quick Quote
Send "product type + diameter + alloy” to receive a formal quote within 2 hours.
Custom titanium rivet solutions
With expertise in raw material selection, manufacturing processes, quality control, and application engineering, we deliver high-quality, high-performance titanium rivets to customers worldwide.

Open End Blind Rivet

Painted Rivets

Peel Blind Rivet

Structural Bulb Tite Blind Rivet

Anlock Blind Rivet In Bolt

Anlock Blind Rivet Out-Bolt

Bulb Tite Blind Rivet

Hem Luk Rivets

High Strength Blind Rivet

Multi Grip Blind Rivet

Sealed Blind Rivet

Drive Rivet
Size selection guide
To help global customers choose quickly, below is a reference of the most common titanium rivet diameters in both inch and metric sizes, along with head type, recommended grip range* (effective clamping thickness), and typical applications.
| Inch diameter | Metric diameter | Common head type | Recommended grip range* | Application examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8″ | Ø3.2 mm | Dome / CSK | 0.4 – 4.8 mm | Electronics housings, lightweight carbon panels |
| 5/32″ | Ø4.0 mm | Dome / Large Flange | 1.0 – 6.4 mm | Marine aluminum panels, enclosure joints |
| 3/16″ | Ø4.8 mm | Dome / Sealed | 1.2 – 9.5 mm | Grade 2 titanium blind rivets 3/16 inch (deck bestseller) |
| 1/4″ | Ø6.4 mm | Dome / Bulbed | 3.2 – 12.7 mm | Structural blind rivets, aluminum vehicle frames |
*Grip range can be adjusted by ±0.4 mm as needed; special lengths available upon request.
Service commitment:
- All sizes meet DIN 7337 / NAS1919 tolerance requirements.
- Random inspection ensures diameter and grip range variation ≤ ±0.05 mm.
- Free PDF size conversion chart and CAD hole dimension drawings provided.
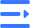
Titanium rivets alloy selection
For rivets, cold workability is the most critical factor—only materials with good cold-forming properties can be installed by cold riveting.
Titanium alloy rivets are typically used in components where lower strength is acceptable but high corrosion resistance is essential.
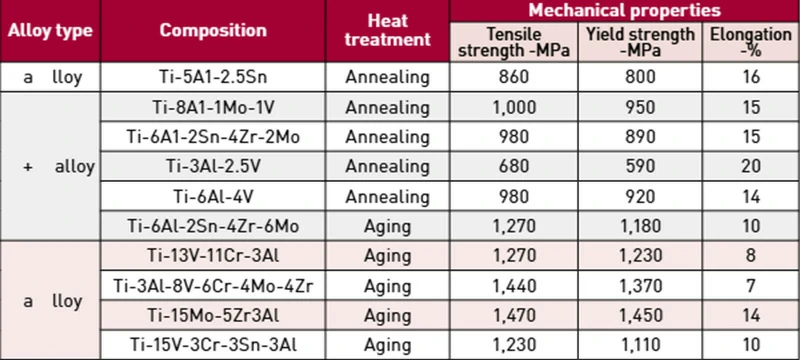
Manufacturing titanium rivets
Processes such as forging, cold heading, CNC machining, and surface treatment work together to ensure titanium rivets meet design requirements while maintaining excellent quality and stability.
Forging
Isothermal die-forging of titanium bars in a vacuum inert atmosphere refines the grain structure, removes inclusions, and creates a dense, high-strength base material for the rivet.
Contact us now

Cold heading
Multi-station, multi-blow cold heading forms the rivet shank and head in one pass, preserving fiber flow lines and controlling dimensional consistency within ±0.02 mm.
Contact us nowCNC machining
Five-axis CNC machines finish micro-countersinks and laser markings in a temperature-controlled environment, holding tolerances to ±0.008 mm. Vacuum stress relief annealing is applied to eliminate residual stresses.
Contact us now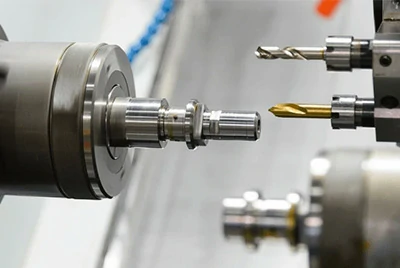

Surface treatment
Pickling and passivation combined with anodizing or MoS₂ dry-film lubrication create a stable TiO₂ layer and a low-friction coating, delivering seawater-grade corrosion resistance and smooth assembly.
Contact us nowTitanium rivet applications
Aerospace & drones
Replacing traditional aluminum solid rivets with aerospace titanium rivets (NAS1919) can boost structural shear strength by about 40 % while reducing overall weight by roughly 35 %.
10⁷ cycle fatigue testing confirms that titanium rivets maintain stable clamping force in lightweight structures such as wing skins, composite spars, and foldable drone arms.
Each batch comes with a NAS part number cross-reference and third-party shear/tensile reports, meeting FAA / EASA airworthiness documentation requirements to help customers complete certification faster.
Marine & offshore
Marine titanium rivets in sealed type pass 1 000 h ASTM B117 salt-spray tests with no red rust or leakage, ideal for aluminum decks, railing bases, and hatch covers.
- Lock-mandrel technology secures the stem to prevent foreign object damage.
- Optional large-flange heads distribute load and prevent thin plate deformation.
- Supplied with salt-spray reports and PED / DNV certificates to ensure smooth classification society approval.
Carbon bicycles & sporting goods
Colored titanium rivets, anodized in blue, purple, gold, or rainbow finishes, enhance visual appeal while retaining seawater-grade corrosion resistance.
At only 55 % of the weight of steel rivets, they are the perfect lightweight fasteners for carbon frame linkages, snowboard metal edges, and premium outdoor gear.
The anodic film is about 0.3 µm thick, preserving fit clearance.
Free color sample packs are available to help designers quickly prototype and confirm color schemes.



Matching titanium fasteners: one-stop sourcing guide
To help you get a complete set of high-performance titanium fasteners in one order, we highly recommend the following products in addition to titanium washers.

Titanium Dowel Pins
We not only supply titanium rivets, titanium bolts, titanium nuts, and titanium screws, but also a wide range of fasteners made from stainless steel, aluminum alloys, copper alloys, Inconel, Hastelloy, Monel, zirconium, tantalum, and other special alloys—covering your multi-material needs in extreme conditions like high temperature, corrosion, and lightweight applications.
If you require custom components, please contact our engineers for tailored support. Quick Quote
How do rivets work?
Rivets can be applied in many ways. Installed rivets are inserted into a hole by drilling, placement, or pressing, and the tail is securely deformed to lock in place.
Typically, the tail is deformed by hammering or squeezing, flattening the material and increasing its diameter. Once hammered, the tail forms a dumbbell-like shape, completing the fastening seamlessly.
People also ask – FAQ
Can titanium be riveted?
Yes. Titanium's ductility is sufficient for cold heading and cold riveting. Choosing α or near-α alloys such as Grade 2 or Ti-5Al-2.5Sn allows one-step forming at room temperature.
For higher strength needs, use titanium blind rivets or titanium solid rivets (NAS1919 series) with dedicated titanium rivet guns. The assembly process is very similar to that for aluminum or stainless steel rivets.
What is the best material for rivets?
"Best” depends on the working environment: carbon steel rivets suit general structures, 316 stainless steel is common for corrosion-resistant applications, and titanium rivets are almost the ideal choice when both light weight and corrosion resistance are required.
They offer shear strength close to 900 MPa while being about 45 % lighter than steel, excelling in aerospace, marine, and premium sporting goods applications.
What is the strongest type of rivet?
For the same diameter, the titanium solid rivet—especially Grade 5 and NAS1919/MS20470 series—provides the highest shear and tensile strength.
When single-side installation is necessary, a structural-grade lock-bulb titanium blind rivet offers strength close to that of a solid rivet thanks to its mechanical lock-core design.
What are the disadvantages of titanium bolts?
The main drawbacks of titanium bolts (including titanium rivets) are higher material costs, faster tool wear during machining, and a tendency to gall under dry friction. Titanium can also cause galvanic corrosion when in direct contact with carbon steel or copper alloys.
However, bulk cold heading can reduce costs, MoS₂ dry-film lubrication minimizes galling, and insulating washers at dissimilar-metal interfaces can prevent galvanic corrosion—ensuring titanium fasteners remain cost-effective over their service life.
How to install solid rivets
Installing solid rivets requires specific tools and steps:
- Prepare solid rivets, a drill with the matching bit, deburring/chamfering tools, a rivet hammer and bucking bar (or pneumatic rivet gun), and safety gear.
- Mark rivet hole positions, align the two workpieces, and clamp them securely.
- Drill through with a bit matching the rivet diameter, deburr both sides, and countersink if using flush rivets.
- Ensure the rivet tail protrudes at least 1.5 times the rivet diameter beyond the base material.
- Insert the rivet into the hole and strike the head with the rivet hammer (or use a rivet gun) while the bucking bar provides counterforce, plastically deforming the tail into a dome.
- Inspect the finished head to ensure symmetry, no cracks, and a tight, secure joint.
Can solid rivets be removed after installation?
If solid rivets need to be removed, it is generally not recommended as this may damage the joined materials.
When removal is unavoidable, a special tool called a rivet remover can be used to drill them out.
However, this process can be time-consuming and may cause damage to the surrounding material.