Gr2 vs Gr5 Titanium
Updated : Oct. 30, 2025Need to quickly choose the right titanium grade for seawater/chemical or aerospace/medical applications?
This page provides a one-glance comparison of Titanium Grade 2 vs Grade 5 in terms of Composition, Mechanical/Thermal Properties, Corrosion / Welding / Machining, along with ASTM / AMS standards, EN 10204 3.1 certification, available sizes, and a 3-step material selection guide.
Read in 3 minutes, know whether to choose GR2 or GR5, and move straight to quotation or ordering.
One-Chart Quick Comparison
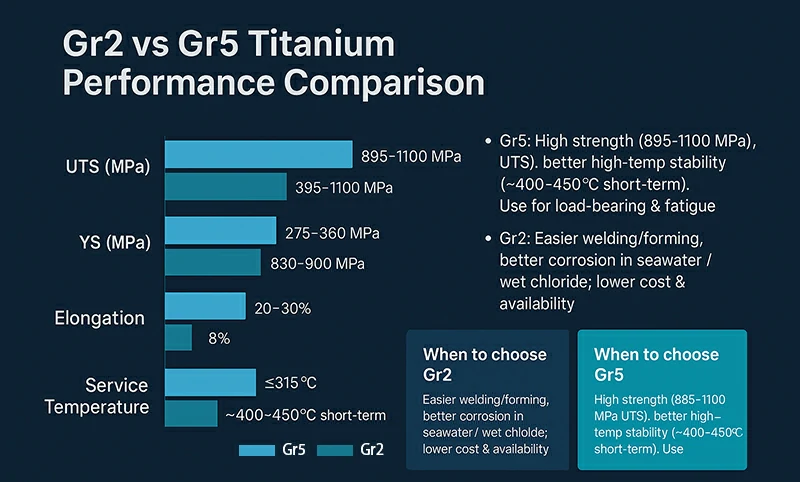
Strength (UTS / YS): Gr5 ≈ 895–1100 / 830–900 MPa; Gr2 ≈ 345–420 / 275–360 MPa
→ For load-bearing and fatigue-critical parts, Gr5 is preferred.
Elongation: Gr2 ≈ 20–30%, Gr5 ≈ 8–14%
→ Gr2 offers better formability and welding tolerance.
Service Temperature: Gr2 typically ≤ ~315 °C; Gr5 up to ~400–450 °C short-term
→ Gr5 maintains strength better at higher temperatures.
Corrosion Resistance: Gr2 is more stable in seawater and wet chlorine environments; Gr5 requires galvanic corrosion isolation when in contact with dissimilar metals.
Manufacturing Feasibility (Welding / Machining): Gr2 has a wider welding window; both are difficult to machine, Gr5 is harder—use low speed, sufficient cooling, and sharp tooling.
Cost & Availability: Gr2 is more economical and widely available; Gr5 is higher in unit price and demands tighter control in processing and lead time.
Grade 2 vs Grade 5 Chemical Composition
| Element | Grade 2 (%) | Grade 5 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | Bal. | Bal. |
| Al | — | 5.50–6.75 |
| V | — | 3.50–4.50 |
| Fe | ≤0.30 | ≤0.40 |
| O | ≤0.25 | ≤0.20 |
| C | ≤0.08 | ≤0.08 |
| N | ≤0.03 | ≤0.05 |
| H | ≤0.015 | ≤0.015 |
| Others (each) | ≤0.10 | ≤0.10 |
| Others (total) | ≤0.40 | ≤0.40 |
Grade 2 is a single-phase α (Alpha) titanium, offering better ductility and a wider welding window. It is suitable for seawater, chemical processing, and heat exchanger applications.
Grade 5 is a dual-phase α + β titanium alloy and can be solution-treated and aged, offering higher strength and high fatigue life, making it ideal for aerospace structures, fasteners, and medical components.
Grade 2 vs Grade 5 Physical Properties
| Property (Metric) | Grade 2 (CP Ti) | Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 4.50–4.51 | 4.42–4.43 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | 103–110 | 110–114 |
| Shear Modulus (GPa) | ≈44 | ≈44 |
| Poisson's Ratio (ν) | ≈0.34 | ≈0.34 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K, 20°C) | 15–22 | 6.5–7.2 |
| Specific Heat (J/kg·K, 20°C) | ≈520 | ≈560 |
| Electrical Resistivity (µΩ·cm, 20°C) | 42–46 | 165–175 |
| CTE (µm/m·K, 20–100°C) | 8.4–8.8 | 8.6–9.2 |
| Melting Point (°C) | ≈1668 | ≈1604–1660 |
- Heat Transfer / Electrical Properties: Gr2 has higher thermal conductivity (15–22 W/m·K) and lower electrical resistivity (42–46 µΩ·cm); Gr5 has lower thermal conductivity (~6.5–7.2 W/m·K) and higher resistivity (~165–175 µΩ·cm) → Gr2 is preferred for heat exchangers and electrochemical stability.
- Stiffness: Both have similar elastic modulus (~110 GPa); overall structural rigidity is mainly influenced by section geometry and heat treatment.
- Thermal: Coefficient of thermal expansion is close for both (8.4–9.2 µm/m·K); Gr5 has a slightly lower melting range compared to commercially pure titanium.
Grade 2 vs Grade 5 Mechanical Properties
| Property (Metric) | Grade 2 (CP Ti) | Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) |
|---|---|---|
| Ultimate Tensile Strength UTS (MPa) | ≥344 | ≥895 |
| Yield Strength YS 0.2% (MPa) | ≥275 | ≥828 |
| Elongation (%) | ≥20 | ≥10 |
*Mechanical property data according to ASTM B348 / ASTM B265 (annealed condition, minimum values). Actual requirements shall follow the contract or purchase specification.
If you are in seawater / chemical applications: Grade 2 is easier to form and weld, helping reduce manufacturing and maintenance costs.
If you are in aerospace / fasteners / medical applications: Use Grade 5 as the baseline for strength and fatigue performance, making lightweight design easier to achieve.
If budget or delivery time is limited: As long as strength and temperature conditions permit, first evaluate Grade 2 in-stock options; otherwise, choose Grade 5 and manage welding/machining risks during design.
Grade 2 vs Grade 5 – Corrosion, Welding and Machining Feasibility
Corrosion
In seawater, wet chlorine and chloride-containing environments, Grade 2 forms a more stable passive film, with lower risk of pitting and crevice corrosion. It is well-suited for long-term use in heat exchangers and fluid equipment.
When higher strength is required in chemical media, Grade 5 may be considered, but galvanic corrosion must be addressed during design—such as using fasteners of the same material, insulating gaskets or coating barriers, and minimizing stagnant zones and crevice structures.
For strong reducing acids, fluoride-containing media or high-temperature dry chlorine, neither Grade 2 nor Grade 5 is recommended for direct use; a case-by-case evaluation is required before confirmation.
Welding
Grade 2 offers a wider welding window and higher tolerance to on-site conditions; Grade 5 requires strict control of heat input and shielding gas quality. In engineering practice, TIG (GTAW) is preferred, using high-purity argon with sufficient trailing shield and backside purging. Before welding, joint surfaces must be cleaned of oil and oxide layers, and assembly gaps should be uniform.
Recommended filler metals: ERTi-2 for Grade 2, ERTi-5 for Grade 5; for dissimilar welding, follow the lower-strength side.
A qualified weld should appear silver to light straw yellow; blue, purple or dark discoloration indicates overheating—reinspection and rework are required.
For pressure-bearing or critical components, establish WPS/PQR according to AWS D17.1 / ISO 15614-5, and ensure density using PT or helium leak testing.
Machining
Both grades tend to gall and cause work hardening, more severe in Grade 5. Therefore, machining must follow the principles of low cutting speed, high feed rate, shallow depth of cut, and sufficient cooling. Use sharp PVD-coated carbide tools, rigid fixturing, and avoid air cutting or pauses that increase frictional heating.
During turning, milling, or drilling, chip control must remain stable; drilling should use short drills with high-pressure coolant and step retraction for chip removal. Pre-chamfering the hole entry reduces burrs and edge chipping.
For automated batch feeding, TGP precision-ground bars with double-end chamfering are recommended to improve feeding reliability and dimensional stability.
For Grade 5, cutting speed should be further reduced and tool engagement time shortened to control heat accumulation and tool deflection, ensuring stable surface finish and tolerance control.
Grade 2 vs Grade 5 Typical Applications
Grade 2(CP Ti)
- Seawater desalination and offshore engineering: Maintains stability during long-term immersion in chloride-containing environments, resulting in longer maintenance intervals.
- Chemical processing: Used for equipment linings and fluid passages under acidic/chloride conditions to reduce pitting and crevice corrosion.
- FGD desulfurization and power flue gas systems: Performs better than most alloy steels in sulfur- and chlorine-containing wet environments due to strong corrosion and scaling resistance.
- Pulp bleaching section: Excellent resistance to wet chlorine media, reducing downtime.
- Seawater heat exchangers: Maintains heat transfer efficiency in chloride environments while minimizing leakage risks.


Grade 5(Ti-6Al-4V)
- Aerospace structures and fasteners: High strength-to-weight ratio, ideal for load-bearing components requiring lightweight performance.
- Engine casings and high-temperature peripheral components: Superior strength retention at medium to elevated temperatures; used in areas close to engine hot zones.
- Medical implants and surgical instruments: Combines high strength with biocompatibility and excellent fatigue life.
- Motorsport and high-performance machined parts: Maintains dimensional and strength stability under high-impact and high-cycle loading.
- High-end tooling and fixtures: Suitable for components requiring high stiffness, wear resistance, deformation control, and extended service life.

Chalco Titanium – Available Products
We don't just compare — we supply directly. All products are manufactured according to ASTM / AMS / EN standards, delivered with EN 10204 3.1 certificates. Chemical, mechanical, dimensional and ultrasonic testing are available. We offer stock materials, cut-to-length service, TGP precision grinding, global shipping, and engineering support based on drawings and operating conditions. Typical sizes can be sampled within two weeks.
Already selected the material? Click the internal links below to request a quotation.
Grade 2(CP Ti)
Designed for seawater, chemical processing, FGD and other corrosion-resistant applications. Supplied as plate/pipe/bar/forging under ASTM standards, with optional AWS / ISO welding documentation and third-party inspection. Supports cut-to-length, beveling/chamfering and precision grinding. Stock-friendly and fully traceable by batch.
Grade 5(Ti-6Al-4V)
Serves aerospace, fasteners, medical components and high-strength lightweight applications. Supplied per ASTM B348 / B265 / B381 and AMS 4928 / 4911. Available in annealed (Annealed) or solution-treated and aged (STA) conditions, with ultrasonic, dimensional and surface consistency control.

Grade 5 Titanium Plate

Grade 5 Titanium Tube

Grade 5 Titanium Round Bar

Grade 5 Titanium Square Bar

Grade 5 Titanium Wire

ERTi-5 Titanium Welding Wire
FAQ
Is Grade 5 always better than Grade 2?
Not necessarily. Choose Gr5 if you require high strength, high temperature resistance or high fatigue life; choose Gr2 for seawater/wet chlorine environments, better formability and weldability, and lower cost.
Can Grade 5 be used in seawater?
Yes, but galvanic corrosion isolation and cost evaluation are required. In most seawater systems, Gr2 is the more stable and preferred option.
Are there differences in welding difficulty?
Yes. Gr2 has a wider welding window, while Gr5 requires strict control of heat input and shielding gas. It is recommended to establish WPS/PQR according to AWS D17.1 / ISO 15614-5.
Is machining stable for mass production?
Both grades tend to gall and work-harden; Gr5 is more sensitive. Use low cutting speed, high feed, shallow depth of cut, sufficient cooling, and preferably TGP precision-ground bars with double-end chamfering.
What standards do you supply to and what documents are included?
ASTM B265 / ASTM B338 / ASTM B348 / ASTM B381; Gr5 also supports AMS 4928 / 4911. Delivery includes EN 10204 3.1 certificates and inspection reports (chemical, mechanical, dimensional, ultrasonic).
What about lead time and minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
Regular sizes are available from stock with cut-to-length service. Typical sizes can be sampled in about two weeks. MOQ depends on dimensions and processing requirements—just send your list for confirmation.
What factors influence the price?
Alloy grade, dimensions and condition (Annealed / STA), processing services (TGP, chamfering, machining), inspection level, and delivery urgency.
How to select the right grade in three steps?
Check the medium (strong corrosion → Gr2)
Check mechanical strength / temperature (high strength / high temperature → Gr5)
Verify manufacturing feasibility and budget
Can you provide third-party inspection and traceability?
Yes. We support ultrasonic testing (ASTM B594), dimensional and surface roughness control, full batch traceability, and third-party witness inspection.
Still not sure which grade to choose?
Send us your operating conditions (medium / temperature / stress / dimensions / annual usage), and our engineers will return a feasible material and specification proposal within 24 hours.